
The AMD Ryzen 7 8700G is a top-tier processor in the Ryzen 8000G series, tailored for desktop platforms. It’s renowned for its exceptional performance, particularly in gaming and integrated graphics, making it an ideal choice for entry-level gaming PCs.
Key Specifications:
- The processor features 8 cores and 16 threads, ensuring efficient multitasking and handling of demanding applications.
- It operates at a base clock speed of 4.2 GHz and can boost up to 5.1 GHz, delivering robust performance.
- The Ryzen 7 8700G is built on a 4nm TSMC FinFET process, enhancing its efficiency and power management.
- It supports DDR5 memory with a dual-channel interface, with officially supported memory speeds up to 5200 MT/s. Overclocking capabilities allow for even higher memory speeds, depending on the memory modules used.
- The processor includes a substantial 16MB of L3 cache and an 8MB L2 cache, contributing to its quick data access and processing abilities.
- It features the AMD Radeon 780M integrated graphics with 12 graphics cores and a graphics frequency of 2900 MHz, offering impressive graphical performance without the need for an external GPU.
- The TDP (Thermal Design Power) of the Ryzen 7 8700G is 65W, which is typical for modern PC processors. It also supports a configurable TDP range of 45-65W.
- For connectivity, it utilizes a PCI-Express Gen 4 connection, ensuring compatibility with a wide range of peripherals and components.
- The processor supports advanced instruction sets like AVX, AVX2, and AVX-512, beneficial for calculation-heavy applications.
- The Ryzen 7 8700G is compatible with the AMD Socket AM5 and includes a Wraith Spire cooler in the box.
This processor is a strong contender for users seeking a balance between high-performance gaming and general computing tasks, especially where graphics capabilities are a priority.
AMD Ryzen 8000G Series Unveiled: Exploring the Cutting-Edge 8700G, 8600G, 8500G, and 8300G Processors with Advanced Zen 4, RDNA 3, and AI Capabilities
The AMD Ryzen 8000G series, including the Ryzen 7 8700G, Ryzen 5 8600G/8500G, and Ryzen 3 8300G, offers a range of processors tailored for various computing needs.
- Ryzen 7 8700G: This is the premium model in the series, featuring 8 cores and 16 threads. It boasts a 5.1GHz boost clock, 24MB cache, and the Radeon 780M graphics with 12 cores. Priced at $329, it’s designed for high-performance computing and gaming.
- Ryzen 5 8600G: Positioned as a mid-range option, it has 6 cores and 12 threads, with a 5.0GHz boost clock and 22MB cache. It integrates the Radeon 760M graphics with 8 cores, priced at $279. This processor offers a balance of performance and price, suitable for mainstream users.
- Ryzen 5 8500G: Similar in core count to the 8600G, the difference lies in its graphics unit – the Radeon 740M. This model is an economical choice for those who need decent performance without the need for more advanced graphics capabilities.
- Ryzen 3 8300G: Targeted at the entry-level segment, this processor is primarily for OEMs. It features 4 cores and 8 threads, a 4.9GHz boost clock, and a 12MB cache, along with Radeon 740M graphics. It’s expected to be released by partner manufacturers at the end of the first quarter.
The entire Ryzen 8000G series is based on the Zen 4 architecture, with the 8700G and 8600G models additionally featuring Ryzen AI and XDNA NPU capabilities. They also share the same 65W TDP. The 8500G and 8300G models differ by incorporating a Zen 4 + Zen 4c hybrid architecture.
These processors are designed to cater to a wide range of users, from those seeking top-tier gaming and computing performance to those needing basic computing capabilities. The integrated graphics in each model vary according to their positioning in the market, offering suitable options for different levels of graphical performance needs.
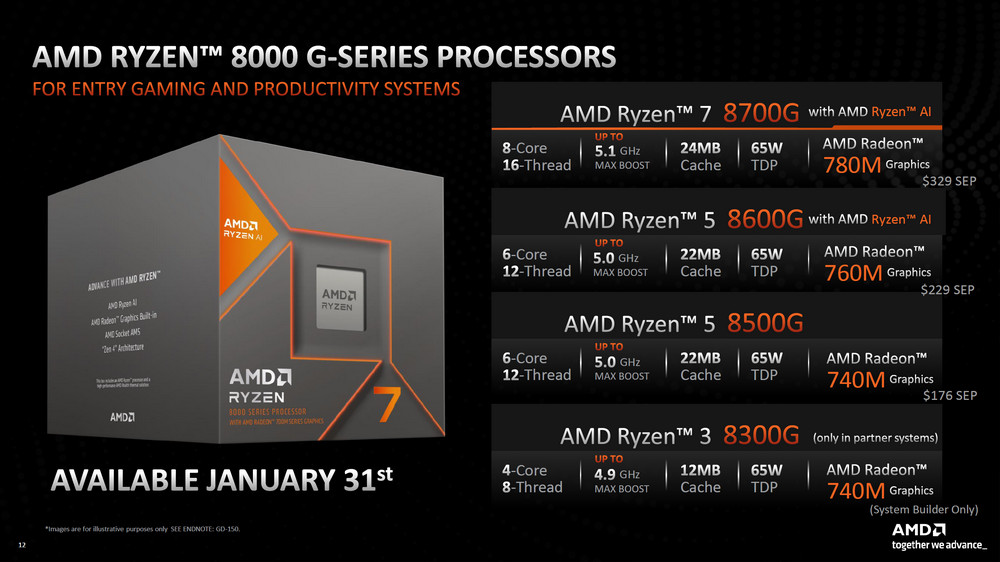
The uploaded image appears to be an official AMD marketing graphic for the Ryzen™ 8000 G-Series processors, designed for entry-level gaming and productivity systems. The graphic showcases the range of processors within the series along with their specifications:
- AMD Ryzen™ 7 8700G: Positioned as the leading model in the series with 8 cores and 16 threads, a maximum boost clock of 5.1 GHz, 24MB of cache, and Radeon™ 780M graphics. It has a 65W TDP and is priced at $329 SEP.
- AMD Ryzen™ 5 8600G: A mid-tier option with 6 cores and 12 threads, up to a 5.0 GHz max boost clock, 22MB of cache, and Radeon™ 760M graphics. It shares the same 65W TDP and is set at $229 SEP.
- AMD Ryzen™ 5 8500G: This variant also offers 6 cores and 12 threads, a 5.0 GHz max boost clock, 22MB of cache, but comes with Radeon™ 740M graphics. It has a 65W TDP with a price point of $176 SEP.
- AMD Ryzen™ 3 8300G: The entry-level model is available only in partner systems, featuring 4 cores and 8 threads, up to a 4.9 GHz max boost clock, 12MB of cache, and Radeon™ 740M graphics. It also has a 65W TDP and is designated for system builders only.
The graphic emphasizes the integration of AMD Ryzen™ AI across the higher-end models and highlights the consistent TDP of 65W across the series, suggesting a balanced combination of performance and power efficiency. The date of availability is mentioned as January 31st, which indicates the date the processors were or will be available to the public.
This lineup illustrates AMD’s commitment to providing a diverse range of processing solutions to meet various user requirements, from high-end gaming to basic productivity tasks, with integrated graphics options scaling accordingly.
Based on the specifications and architecture, it’s understood that while the new Ryzen 8700G and Ryzen 8600G processors may have slightly lower CPU performance compared to their counterparts, the Ryzen 7700 and Ryzen 7600 respectively, they offer advanced integrated graphics capabilities.
The Ryzen 8700G and 8600G are equipped with the latest RDNA 3 architecture for their integrated graphics, which is a significant upgrade from the basic RDNA 2 2CU integrated graphics found in the general Ryzen 7000 series processors. The RDNA 2 integrated graphics in the Ryzen 7000 series are adequate for basic tasks such as system boot, diagnostics, and debugging.
On the other hand, the Ryzen 8500G and 8300G feature a combination of Zen 4 and Zen 4c cores. This mix of core types, often referred to as a hybrid or “big.LITTLE” architecture, is designed to balance performance and energy efficiency by allocating tasks between high-performance and high-efficiency cores.
For gamers or users who prioritize graphical performance, the Ryzen 8700G and 8600G would be the recommended choices due to their superior RDNA 3 integrated graphics, which should provide a better gaming experience and higher performance in graphics-intensive applications compared to the Zen 4 + Zen 4c configurations of the 8500G and 8300G.
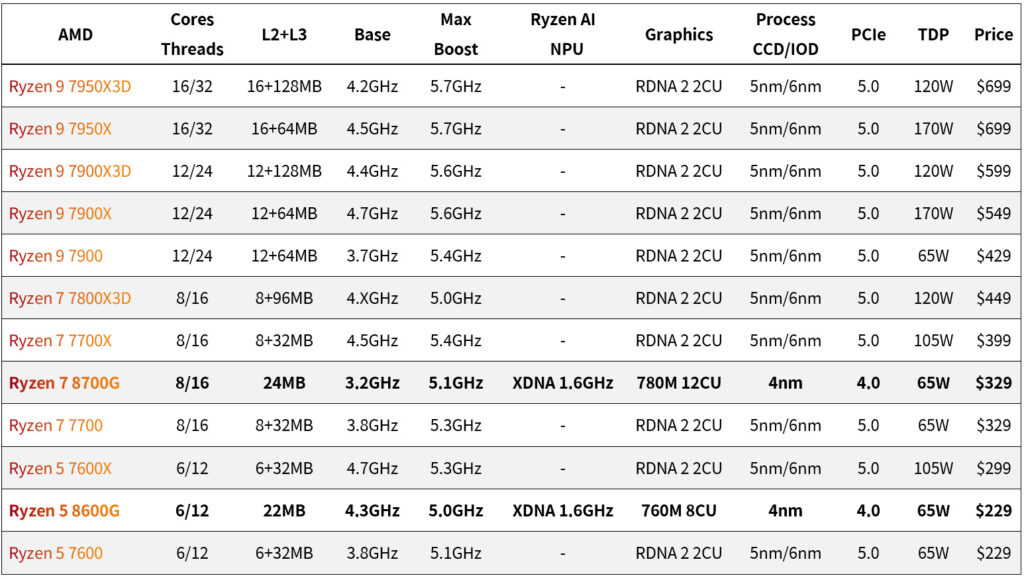
A comparative specification chart for the AMD Ryzen 7000 and 8000 series processors.
The Ryzen 7 8700G is featured as an 8-core, 16-thread processor with 24MB of L2+L3 cache, a base clock of 3.2GHz, and a boost clock of up to 5.1GHz. It’s distinct from the rest of the Ryzen 7000 series with its integration of XDNA at 1.6GHz and the Radeon 780M graphics with 12 Compute Units (CUs). It is manufactured on a 4nm process and supports PCIe 4.0 with a TDP of 65W, priced at $329.
In comparison, the Ryzen 7 7700X, with the same core and thread count, offers higher base and boost clocks (4.5GHz and 5.4GHz, respectively) but uses the older RDNA 2 graphics with 2 CUs, built on a 5nm/6nm process, supports PCIe 5.0, and has a TDP of 105W, priced at $399.
The Ryzen 5 8600G, another processor from the 8000 series, offers 6 cores and 12 threads with a total of 22MB of L2+L3 cache. It has a base clock of 4.3GHz and a boost clock of up to 5.0GHz, also incorporates the XDNA at 1.6GHz and comes with Radeon 760M graphics with 8 CUs. It shares the 4nm process, PCIe 4.0 support, 65W TDP, and is priced at $229.
These specifications suggest that while the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G may offer slightly lower base and boost CPU clocks compared to their 7000 series counterparts, they bring significantly enhanced integrated graphics performance with the RDNA 3 architecture. This makes them potentially more appealing for users who rely on integrated graphics for gaming or creative applications, as opposed to the Ryzen 7000 series processors which might be more suitable for users with dedicated GPUs.
The Ryzen 7000 and 8000 series present a diverse lineup, enabling users to choose processors based on their specific needs, whether it’s CPU performance, integrated graphics capabilities, power consumption, or price point.
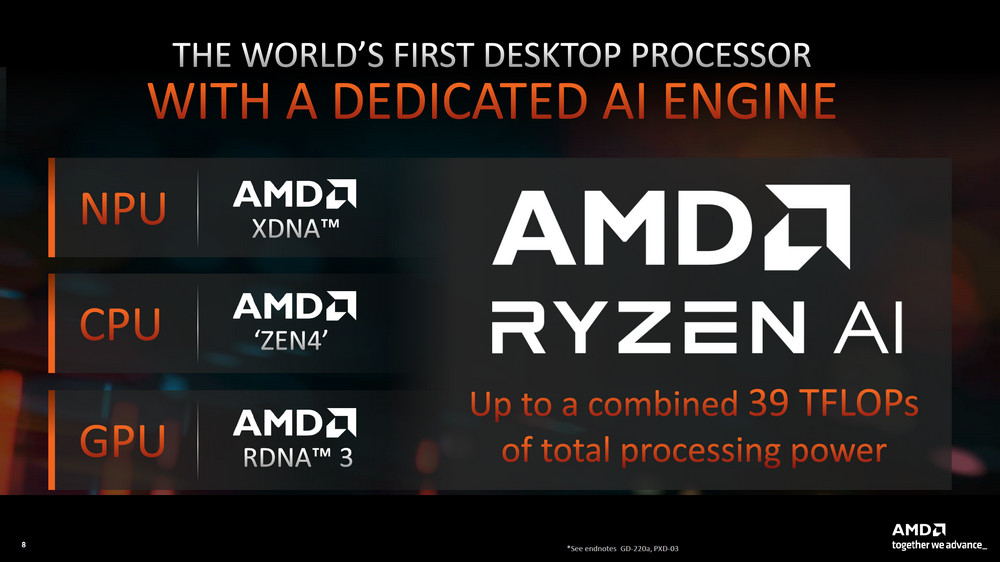
The innovative features of AMD’s Ryzen 8000G series processors, notably the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G, which are distinguished by their inclusion of a dedicated AI engine. This feature is a significant step forward for desktop processors, marking AMD’s advancement in integrating AI capabilities directly onto the CPU.
Key Features:
- The AI engine is built on AMD’s proprietary XDNA architecture, which is designed to accelerate AI processing.
- The combined processing power of the CPU, GPU, and NPU (Neural Processing Unit) can deliver up to 39 TFLOPs, a measure of the processor’s computing performance.
- The CPU is based on the Zen 4 architecture, while the GPU leverages the RDNA 3 architecture.
The AI acceleration is positioned to enhance applications that utilize AI features, such as video effects in Microsoft’s suite of applications, Adobe’s creative software, DaVinci’s video editing tools, and video conferencing apps like Zoom. These applications can benefit from dedicated AI processing to deliver more advanced features and improved performance.
While AI applications in PCs are still in an evolving phase, with many applications currently preferring to utilize GPU processing for AI tasks, the introduction of dedicated AI processors like the Ryzen AI represents a pioneering move in the desktop PC market. It suggests a commitment to fostering the growth of AI applications in everyday computing tasks, potentially altering the landscape of how AI is used in both entertainment and productivity contexts.
For entry-level gamers and general users, the immediate benefits of AI acceleration might not be a primary consideration, but it’s an indication of the direction in which the industry is heading. The development of AI applications for lifestyle and productivity will be interesting to watch, as these processors could pave the way for new features and functionalities in the computing experience.

An overview of the vast array of AI-driven software applications and enhancements that are supported by AMD Ryzen™ AI technology. Here’s an overview of the applications and the AI features they leverage:
- Microsoft Studio Effects: AI effects for video conferencing that include blurring, portrait blur, eye gaze correction, and automatic framing. These features enhance video calls, making them more professional and engaging.
- Adobe: A suite of digital editing tools leveraging AI to improve image and audio through automated processes, object selection, neural filters, and content-aware functionalities. Adobe’s AI-powered tools are known for significantly streamlining and enhancing the creative workflow.
- Topaz Labs: Offers video and photo processing techniques and algorithms designed to optimize and enhance visual content. This includes stabilization, cropping, and various levels of image quality adjustments.
- DaVinci: Known for advanced video and audio editing features, including color correction, stabilization, object masking, scene detection, and various effects and enhancements.
Other software includes:
- Boris FX: Video quality upscaling and denoising.
- Zoom: Video call effects and background effects.
- Blender: Generative texturing.
- Avid, Audacity, ByteDance, and CyberLink: Various audio and video editing tools.
- Luminar: AI photo editing.
- Arkrunr, OBS Studio, and XSplitVCam: Live streaming and video enhancement tools.
- MAGIX Vegas: Image editing and upscaling.
These applications demonstrate the broadening scope of AI integration into consumer and professional software, offering advanced features that improve efficiency and creativity in multimedia production. The AMD Ryzen™ AI technology is positioned to enhance these experiences by providing the necessary processing power to handle these sophisticated AI tasks.
Performance Test Analysis: AMD Ryzen 7 8700G & Ryzen 5 8600G with ROG Strix B650-A Gaming WIFI and G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo DDR5-6400
The performance of AMD Ryzen processors, particularly APUs like the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G, can significantly benefit from using high-frequency system memory. DDR5 memory, like the G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo 16GBx2 DDR5-6400 mentioned, can indeed enhance the integrated GPU (iGPU) performance in these processors.
Tests have shown that faster DDR5 memory impacts benchmarks positively, with improved write and read speeds, which in turn can contribute to better overall system performance. This is particularly relevant for iGPUs because they rely on system memory for their graphics tasks, unlike discrete GPUs that have their own dedicated VRAM.
In the context of the Ryzen 7 8700G, which features an impressive 12 compute units of Radeon 780M graphics, the potential for memory overclocking and the resulting iGPU performance gains are significant. This means that investing in higher-clocked memory could be a worthwhile decision if you’re looking to get the most out of the APU’s iGPU for gaming or other graphics-intensive tasks.
While the high performance of the Ryzen 7 8700G’s iGPU has been acknowledged, it’s important to note that it still may not match the performance of dedicated GPUs. However, for many users and use cases, especially those looking for a compact and efficient system, the APU’s iGPU performance might be quite adequate, especially when paired with high-speed memory.
In summary, if you’re building a system around the Ryzen 7 8700G or Ryzen 5 8600G and you aim to leverage the iGPU for gaming or graphics work, pairing these processors with fast DDR5 memory like the G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo DDR5-6400 can indeed provide a performance boost that could make a noticeable difference in your system’s capabilities.

The retail packaging for the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G processors, along with a box of G.Skill Trident Z5 memory. The packaging for both processors highlights their support for AMD Ryzen AI, indicating the inclusion of advanced AI processing capabilities, which is a key feature of these APUs. The presence of the G.Skill Trident Z5 memory suggests high-performance DDR5 RAM, which as discussed earlier, can enhance the iGPU performance of the APUs when paired together in a system build. The ROG Strix box in the background suggests that the motherboard model ROG Strix B650-A Gaming WIFI is part of this setup, providing a robust platform for these components to operate together optimally.
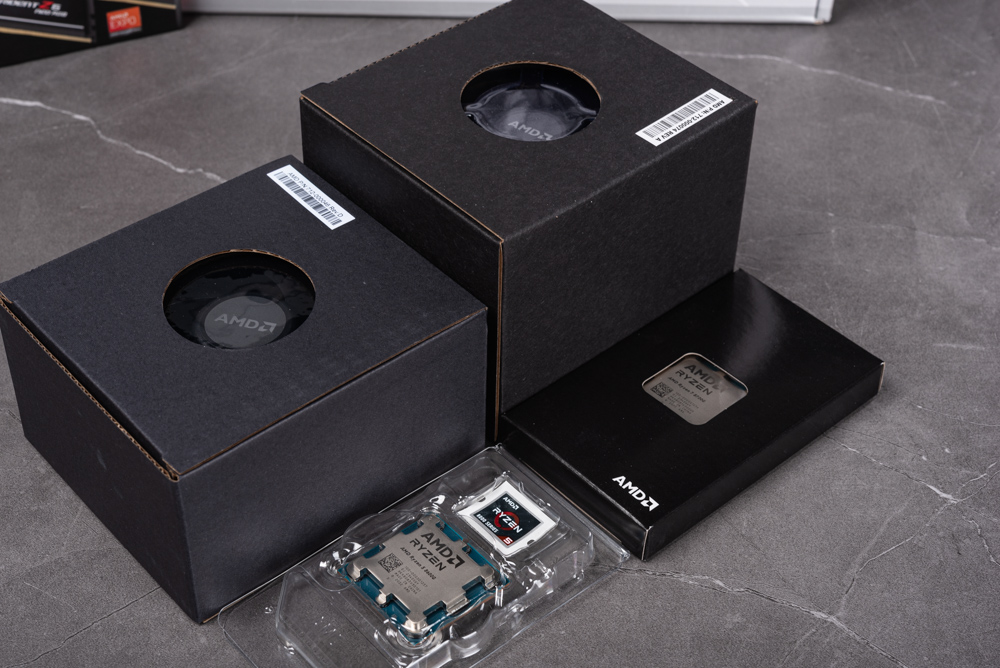

The image provided shows two processors, presumably the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G, alongside their respective boxes, which appear to include the stock coolers. The presence of stock coolers is a typical practice by AMD, especially with their APU line, as these processors are often used in settings where third-party coolers are not preferred due to space, budget, or complexity considerations.
Stock coolers provided by AMD, like the Wraith series, are known to offer adequate cooling performance for the processors under typical operating conditions. They are designed to match the TDP (Thermal Design Power) of the CPUs they accompany, ensuring that the processors can run at their base clock speeds without thermal throttling under standard workloads.
This inclusion is particularly beneficial for users looking to build a system without incurring additional costs for aftermarket cooling solutions and who don’t plan on aggressive overclocking, which typically demands more robust cooling. The stock coolers also simplify the installation process, which can be a plus for those who are new to building PCs or prefer a more straightforward setup.
The AMD Ryzen 7 8700G is paired with the higher-performing Wraith Spire cooler, while the Ryzen 5 8600G comes with the shorter Wraith Stealth cooler. Both of these coolers are designed to meet the basic cooling requirements of their respective processors under normal operating conditions.
However, for users interested in pushing their CPUs further through overclocking or utilizing features like Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO), it is advisable to consider upgrading to more advanced cooling solutions. A larger tower-style air cooler or a 240mm all-in-one (AIO) liquid cooler would provide the enhanced cooling necessary to maintain lower temperatures under the increased thermal load that comes with overclocking.
Upgrading the cooling system not only helps to maintain better temperatures but also can potentially lead to improved performance by allowing the CPU to maintain higher boost clocks for longer periods. When selecting a cooler for overclocking, it’s important to consider factors such as the size of the cooler, the case compatibility, airflow within the case, and the TDP rating of the cooler to ensure it’s suitable for the intended use.
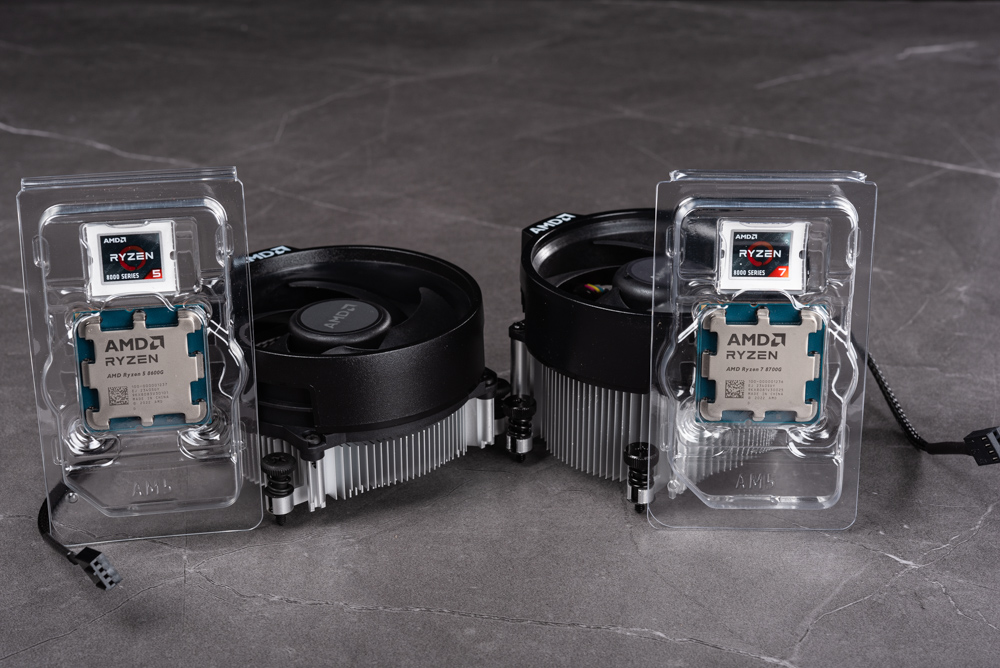

Two AMD Ryzen processors, the Ryzen 5 8600G on the left and the Ryzen 7 8700G on the right, each with their stock coolers. The Ryzen 5 8600G is paired with the Wraith Stealth cooler, a more compact cooling solution, while the Ryzen 7 8700G is accompanied by the larger Wraith Spire cooler, indicative of its higher performance and likely higher thermal design power (TDP).
The Wraith Stealth is generally sufficient for the thermal requirements of the 8600G under standard operation. The Wraith Spire, being larger, provides better-cooling potential, which is suitable for the 8700G with its higher performance capabilities. Both coolers are designed to provide adequate cooling for the processors while operating at stock settings. If users decide to overclock or leverage features like PBO, it might necessitate upgrading to more robust cooling solutions, as you’ve noted.
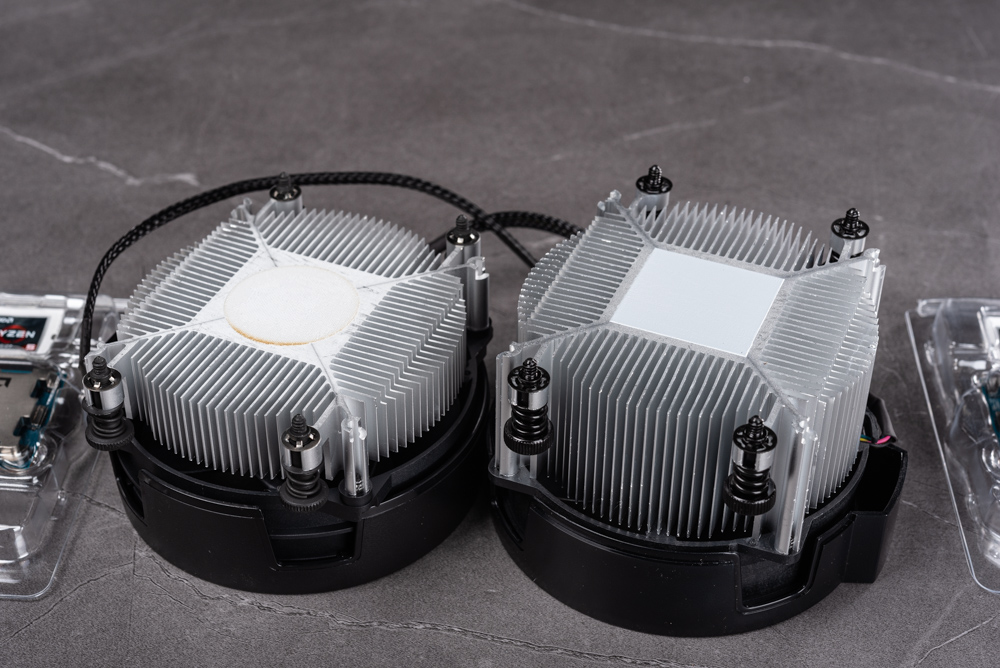

Two AMD stock coolers, both made of aluminum, which is a common material for CPU coolers due to its excellent balance between thermal conductivity and cost. The main difference between the two coolers is their height, which correlates with their cooling capacity.
Taller coolers generally have more surface area for heat dissipation, which can lead to better cooling performance. This is because they can house a larger volume of aluminum fins, which increases the amount of air that can flow through the cooler and the amount of heat that can be radiated away from the CPU.
The cooler with the larger height in the image is likely designed for CPUs with higher TDP (Thermal Design Power), which produce more heat when operating at full capacity or when overclocked. The larger cooler can handle more heat before reaching critical temperatures, making it more suitable for higher-performing CPUs or for users looking to overclock.
On the other hand, the shorter cooler would be appropriate for CPUs with lower TDP and thermal output. It occupies less space inside a computer case, which can be beneficial for smaller builds or systems where space is at a premium.
Both coolers are equipped with a pre-applied thermal paste, indicated by the gray or white compound visible on the base, which helps to facilitate efficient heat transfer from the CPU to the heatsink. The design of these coolers is optimized for AMD’s mounting system, allowing for easy installation on compatible motherboards.

Two processors, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and the Ryzen 5 8600G. These processors are part of AMD’s Ryzen 8000 series, using the AM5 socket with an LGA1718 layout, which requires motherboards with X670, B650, or A620 chipsets for compatibility. They both support DDR5 memory, aligning with the latest advancements in RAM technology for faster and more efficient performance.
Both CPUs offer 20 lanes of PCIe 4.0 connectivity, which is significant for users who may want to install discrete graphics cards. With this configuration, if a dedicated GPU is installed, it would operate at PCIe 4.0 x8 bandwidth. This bandwidth is sufficient for most modern GPUs without causing a bottleneck, ensuring users can take full advantage of their graphics card’s capabilities in addition to the robust integrated graphics that these APUs offer.
The processors are designed to meet the needs of users seeking high performance for gaming, content creation, and productivity, with the added benefit of integrated graphics that are capable of handling some gaming and graphics-intensive tasks without the need for a separate graphics card. The Ryzen 7 8700G, being the higher model, is expected to provide greater performance with more compute units in its integrated GPU compared to the Ryzen 5 8600G.
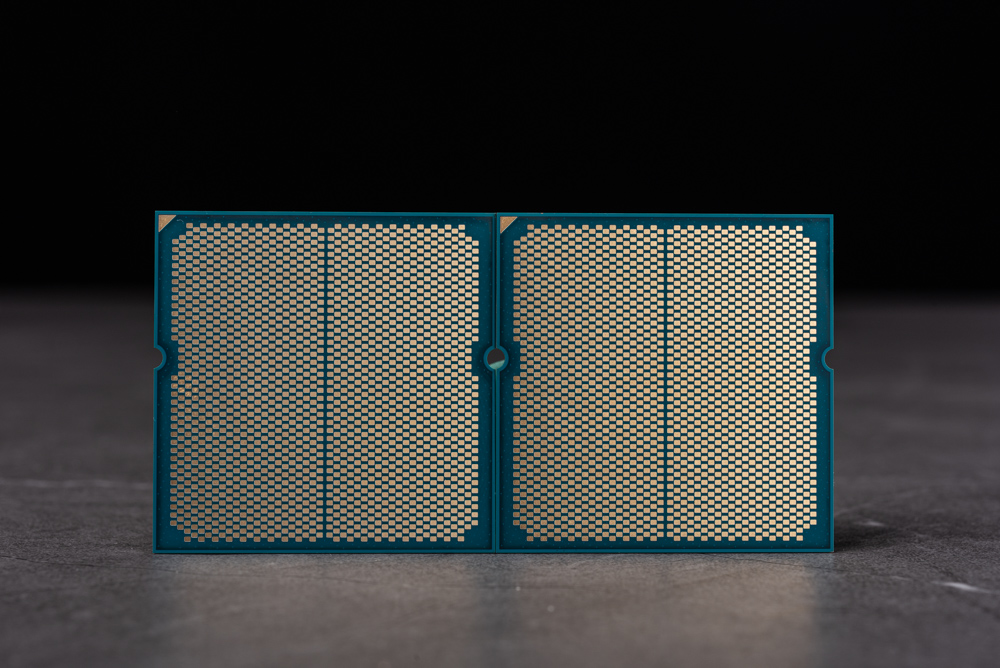
The underside of two CPUs is compatible with the AM5 socket, featuring the LGA1718 contact array. This land grid array (LGA) layout is specific to AMD’s latest CPU socket design, which is used for their newest processors. The LGA1718 socket designates the number of contact points on the CPU, which is 1718 in this case.
The AM5 socket represents a shift from AMD’s previous use of pin grid array (PGA) sockets, where pins were located on the CPU, to the LGA format where pins are in the socket and contact pads are on the CPU. This change aligns with the approach Intel has used for many of its sockets and is significant because it often allows for better power delivery and can potentially offer more robustness during CPU installation, as the risk of bending pins on the CPU is eliminated.
In the AM5 socket, each of the 1718 contact points on the processor interfaces with a corresponding pin in the motherboard socket, ensuring the processor is electrically connected to the motherboard for power, data, and control signals.
The CPUs designed for this socket can take advantage of the latest technologies supported by the AM5 platform, which includes, but is not limited to, PCIe 4.0 connectivity and DDR5 memory, providing a forward-looking foundation for PC builds that aim for high performance and future-proofing.
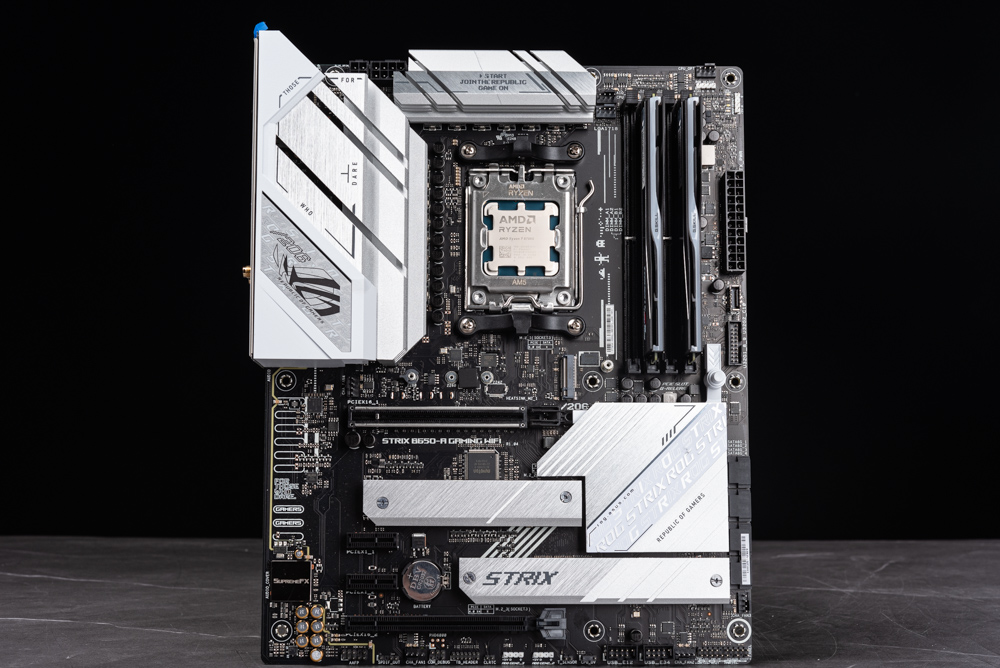

The ROG Strix B650-A Gaming WIFI motherboard is designed for use with AMD’s latest Ryzen processors, including the 8700G and 8600G models. This motherboard is equipped with a 12+2+1 phase 60A power design, which is robust enough to handle high-performance CPUs and provide stable overclocking headroom.
It also features four DDR5 DIMM memory slots, allowing for ample memory capacity and the benefits of the latest DDR5 RAM technology. The black PCB is complemented by silver-white heatsinks and an integrated backplate, which not only aids in cooling but also adds to the aesthetic appeal of the board.
For display outputs, the motherboard includes both HDMI and DisplayPort, which are crucial for utilizing the integrated graphics on processors like the 8700G and 8600G. The PCIe, SATA, and M.2 expansion slot availability may vary depending on the specific PCIe lane allocations of the CPUs used with the motherboard. Since both the 8700G and 8600G provide 20 PCIe 4.0 lanes, the motherboard will allocate these lanes across its various expansion slots and interfaces to balance the connectivity options for graphics cards, storage devices, and other peripherals.
Overall, the ROG Strix B650-A Gaming WIFI is designed to be a versatile platform for gaming and productivity, offering a blend of performance features and connectivity options suitable for a wide range of users.
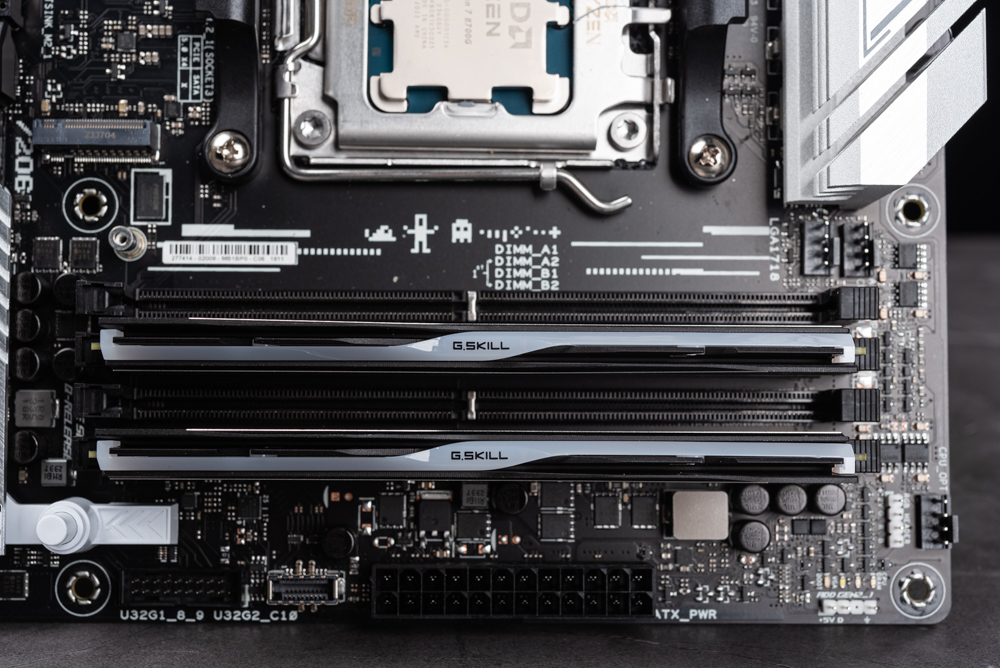

A close-up of the G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo 16GBx2 DDR5-6400 memory modules installed on a motherboard, which appears to be the ROG Strix B650-A Gaming WIFI based on the visible portion of the board. The RAM sticks are slotted into the DIMM slots, and you can see the high-quality heat spreaders that are characteristic of the Trident Z series. These heat spreaders help to dissipate heat efficiently during operation, especially under load or when the memory is overclocked.
DDR5-6400 indicates a very high-speed specification for DDR5 memory, which can significantly benefit overall system performance, particularly in tasks that require high bandwidth and low latency. Faster memory like this is beneficial for systems that rely on integrated graphics, such as those using the Ryzen 7 8700G or Ryzen 5 8600G APUs, as the iGPU uses system RAM for its VRAM, and higher memory speeds can translate to better graphical performance.
The layout of the motherboard also shows attention to detail in design, with clear labeling of the DIMM slots and well-organized placement of components for optimized airflow and cable management. The pairing of this high-performance RAM with a compatible AM5 platform motherboard is indicative of a system build that is targeting high efficiency and performance for gaming, content creation, or other demanding applications.
Comprehensive Test and Comparison: AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G vs. 5700G, 7700, and Intel i7-14700K in Gaming and Performance
In the testing of the AMD Ryzen 8700G and 8600G against the previous generation 5700G and the 65W 7700 processor, as well as the Intel i7-14700K’s integrated graphics. Enabling Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO), using DDR5-6400 EXPO memory, and cooling with a 280mm AIO cooler are excellent choices that should push these CPUs close to their performance limits.
From the benchmarks available, the Ryzen 8700G and 8600G offer competitive performance, showing only a slight reduction in single-core and multi-core performance compared to their Ryzen 7000 series counterparts, despite the reduction in L3 cache capacity. The 8700G seems to trail the Ryzen 7 7700 by just 4.6% in single-core performance and by a mere 2.6% in multi-core tasks. The Ryzen 5 8600G, on the other hand, surpasses its closest counterpart, the Ryzen 5 7600, by about 10.5% in single-core performance and 6.8% in multi-core performance.
In comparison to the i7-14700K, the Ryzen APUs will have different integrated graphics capabilities, with the 8700G likely offering stronger iGPU performance due to its more recent RDNA architecture. It’s important to note that these APUs also bring AI hardware acceleration to the table, which could be a significant advantage in certain applications.
It’s clear that these new APUs will provide a similar level of performance to the 65W Ryzen 7000 series chips in CPU tasks and could potentially offer even better value in the DIY market, considering their integrated graphics performance.
For the most accurate assessment, it’s best to refer directly to the full reviews and benchmarks available on sites like Eurogamer and HotHardware, which provide in-depth analyses and comparisons of these processors in various workloads, including gaming performance.
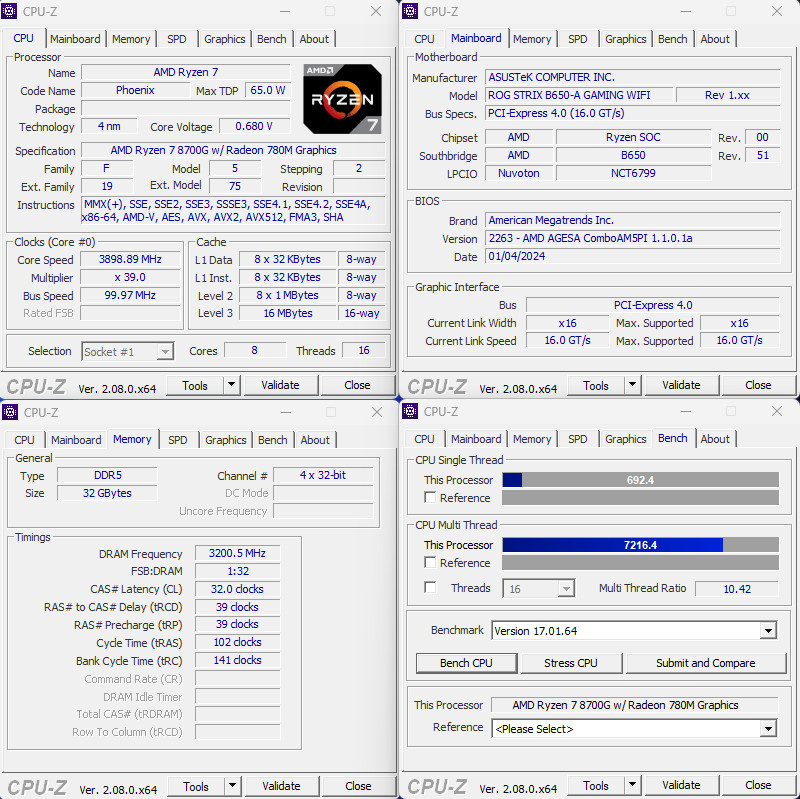
The CPU-Z information provided in the image indicates that the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G processor is built on a 4nm manufacturing process, codenamed Phoenix, and features 8 cores and 16 threads. This aligns with AMD’s approach to offering high-performance computing with increased efficiency thanks to the refined process technology.
In terms of graphics, the GPU-Z data shows the integrated Radeon 780M GPU, which comes with 768 shaders and utilizes 4GB of DDR5 memory, operating at a GPU clock speed of 2900 MHz. This level of GPU specification within an APU suggests a strong performance in integrated graphics, capable of handling various workloads, including gaming and productivity tasks at moderate settings.
The combination of advanced CPU cores and potent integrated graphics with dedicated DDR5 memory, all within a single chip, emphasizes AMD’s commitment to delivering versatile processors that cater to both gamers and creators who may not require a separate graphics card. This APU would be particularly attractive for compact and efficient PC builds where space and power efficiency are priorities.
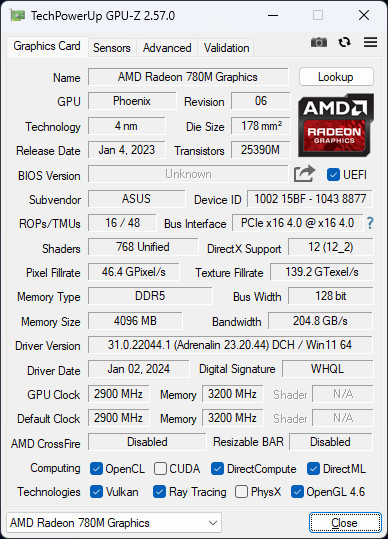
The GPU-Z information presented indicates the AMD Radeon 780M Graphics, which is part of the integrated GPU on the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G APU. According to the data, the Radeon 780M utilizes the Phoenix GPU architecture with a die size of 178 mm² and a total of 25390 million transistors, indicating a highly dense and potentially powerful integrated graphics solution.
Key specifications include:
- Shaders: 768 Unified
- ROPs/TMUs: 16/48
- Memory: 4096 MB DDR5
- Memory Bus Width: 128-bit
- Memory Bandwidth: 204.8 GB/s
- Core Clock: 2900 MHz
- Memory Clock: 3200 MHz (effective)
These specifications suggest that the Radeon 780M is designed to deliver robust performance for an integrated GPU, with a significant amount of shaders and high memory bandwidth that would benefit graphics-intensive tasks. The high core and memory clock speeds indicate that this iGPU is built to handle demanding applications, potentially making it suitable for entry-level gaming and content creation without the need for a discrete graphics card.
The support for DirectX 12, Vulkan, and OpenGL 4.6 also ensures compatibility with a wide range of modern games and graphical applications. However, features like AMD CrossFire, CUDA, and Ray Tracing are not supported, aligning with the typical feature set expected from an integrated GPU.
The data from GPU-Z confirms that the Radeon 780M is a compelling option for users looking for integrated graphics performance in a desktop APU, combining the efficiency of a 4nm process with the power of advanced GPU architecture.
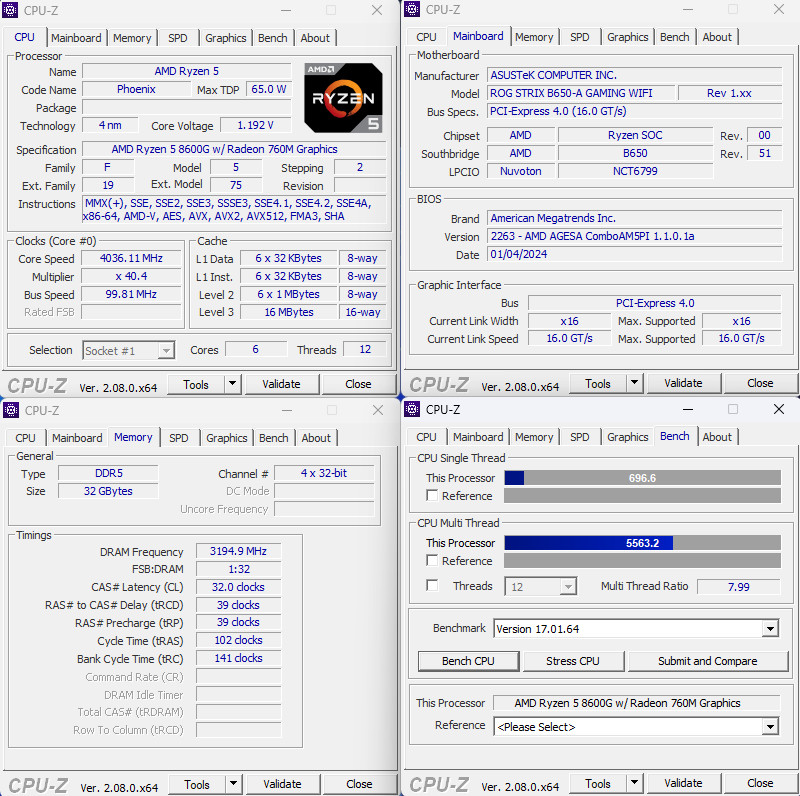
The CPU-Z information for the AMD Ryzen 5 8600G indicates that it is a 6-core, 12-thread processor, utilizing a 4nm manufacturing process and codenamed Phoenix. The additional GPU-Z information reveals that the integrated GPU is the Radeon 760M, which is equipped with 512 shaders and 4GB of DDR5 memory. The GPU clock speed is reported to be 2799 MHz.
This processor sits in AMD’s lineup as a mid-range APU offering, providing solid performance for both general computing and entry-level gaming thanks to its integrated Radeon graphics. The DDR5 memory accompanying the iGPU indicates a strong focus on delivering a capable graphical experience without the need for an additional discrete graphics card.
The Ryzen 5 8600G, with its 6 cores and 12 threads, along with the Radeon 760M graphics, represents a valuable option for users who are looking for a balanced performance in both CPU and GPU tasks. The 4nm process technology used for the CPU should ensure good energy efficiency and potentially lower thermal output, making it suitable for systems where power efficiency and lower heat generation are important.
It’s also worth noting the RAM information from CPU-Z, which shows the system running DDR5 memory at an effective frequency of 3194.9 MHz with timings that are fairly tight for DDR5, indicating the memory is well-suited for high-performance tasks and gaming. This memory configuration can significantly benefit the APU’s integrated graphics performance by providing high-bandwidth memory access, which is critical for iGPU operations.
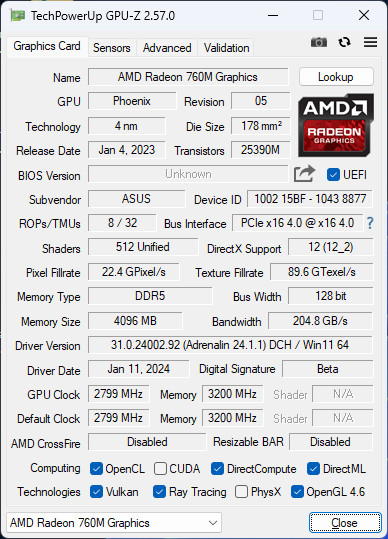
The GPU-Z screenshot provides detailed information about the AMD Radeon 760M Graphics, which is the integrated GPU on the AMD Ryzen 5 8600G APU. Here are the key specifications from the screenshot:
- GPU Name: AMD Radeon 760M Graphics
- GPU Code Name: Phoenix
- Technology: 4nm process
- Release Date: January 4, 2023
- Die Size: 178 mm²
- Transistors: 25.39 billion
- BIOS Version: ASUS
- Shaders: 512 Unified
- ROPs/TMUs: 8/32
- Bus Interface: PCIe x16 4.0 @ x16 4.0
- Memory Type: DDR5
- Memory Size: 4096 MB
- Memory Bus Width: 128-bit
- Bandwidth: 204.8 GB/s
- GPU Clock: 2799 MHz
- Memory Clock: 3200 MHz (effective)
The Radeon 760M iGPU is a significant component of the Ryzen 5 8600G, providing robust graphical capabilities for an integrated solution. The DDR5 memory type with a size of 4GB and a bandwidth of 204.8 GB/s indicates a strong focus on delivering quality integrated graphics performance. The graphics card’s support for technologies like DirectX 12, Vulkan, and OpenGL 4.6 ensures compatibility with modern games and applications.
The information suggests that this iGPU is designed for users who need competent graphics performance for everyday tasks, including casual gaming, content consumption, and productivity applications, all without the need for an additional discrete graphics card.
Breaking Down CINEBENCH 2024 & R23 Results: AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Outshine 5700G and Challenge 7700 in Multi and Single-Core Performance
The performance scores from the CINEBENCH 2024 benchmarking tool, which utilizes the Redshift rendering engine from Cinema 4D. This version is more demanding, with six times the computational load in multi-threaded rendering scenes compared to the R23 version, and accordingly sets higher system requirements for the tests.
Based on these scores:
- AMD Ryzen 7 8700G scored 1074 points in the multi-threaded (nT) test and 112 points in the single-threaded (1T) test.
- AMD Ryzen 5 8600G scored 825 points in the nT test and 110 points in the 1T test.
In terms of performance improvement compared to the previous generation:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G shows a 37% increase in multi-core and a 20% increase in single-thread performance over the Ryzen 5 700G.
- When compared to the Ryzen 7 7700, the 8700G is slightly behind by 8% in multi-threaded and 4% in single-threaded performance.
These results indicate significant advancements in performance for the latest generation APUs, especially in multi-threaded tasks. The slight lag behind the Ryzen 7 7700 in both nT and 1T tests may be due to differences in clock speeds, thermal management, or power limits between the two processors.
It’s important to remember that benchmark scores are only one aspect of overall performance. The real-world effectiveness of a CPU depends on a variety of factors, including software optimization, task-specific architecture advantages, and system configuration. For users who rely heavily on integrated graphics and AI acceleration, the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G could offer more balanced performance, especially considering their improved iGPU capabilities over the previous generation.
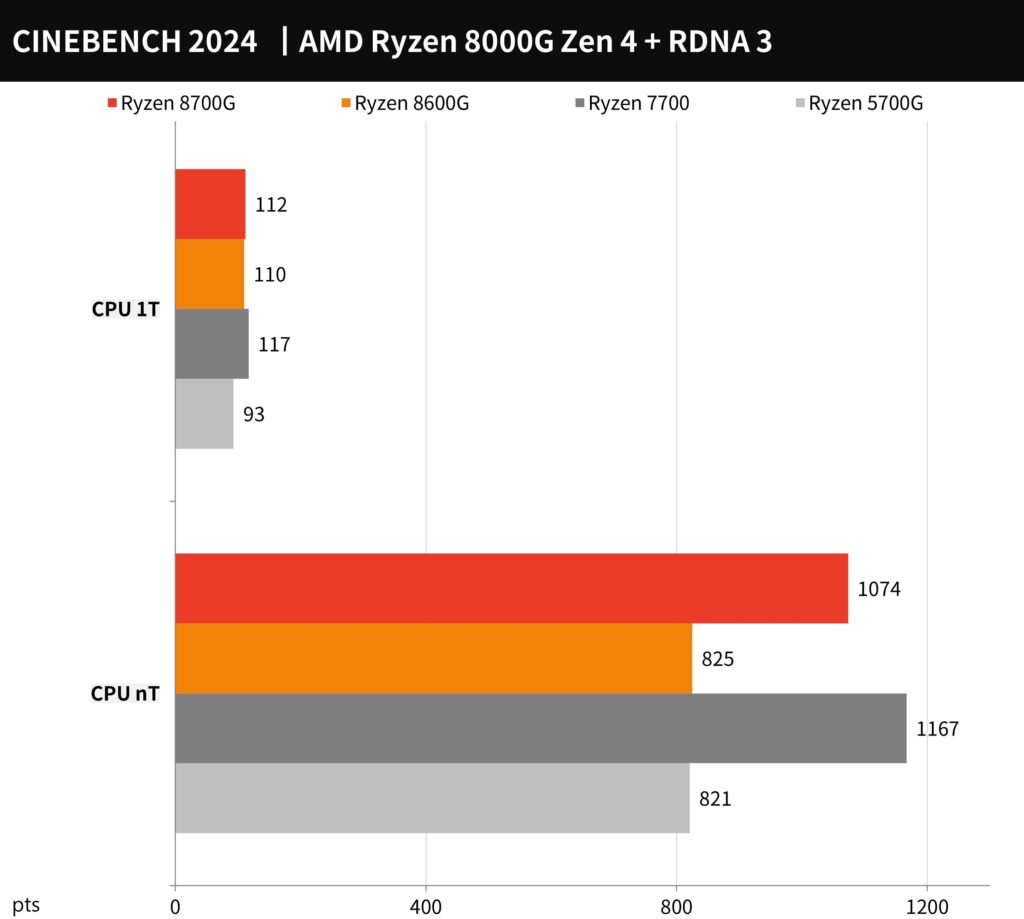
A comparative view of the performance between the AMD Ryzen 8700G, Ryzen 8600G, Ryzen 7700, and Ryzen 5700G processors. In this benchmark, higher scores indicate better performance.
From the provided chart:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G leads in the multi-threaded (nT) test with a score of 1074 points, which is a significant improvement over the Ryzen 5700G’s score.
- In single-threaded (1T) performance, the Ryzen 7 8700G scores 112 points, which is a moderate increase compared to the Ryzen 5700G’s 93 points and slightly behind the Ryzen 7700’s 117 points.
- The Ryzen 5 8600G scores 825 points in the nT test, which is very close to the Ryzen 7700’s 821 points, showcasing competitive multi-threaded performance.
- The Ryzen 5 8600G’s 1T score is 110 points, which is close to the Ryzen 7 8700G’s performance in the same category.
The data indicates that the newer generation APUs, particularly the Ryzen 7 8700G, offer significant improvements in multi-threaded performance compared to the previous generation Ryzen 5 5700G. It also shows that these APUs are competitive with the Ryzen 7700 in multi-threaded tasks, albeit with a slight deficit in single-threaded tasks, which could be due to the differences in clock speeds and other architectural optimizations.
These results can help users gauge the expected performance gains when upgrading from older generations or when choosing between different models for tasks that are either heavily multi-threaded or rely on single-core performance.
For the AMD Ryzen 8700G and Ryzen 8600G show a solid performance uplift compared to the previous generation and a respectable comparison with the same-core-count Ryzen 7700. Here’s a summary of the performance metrics:
- Ryzen 7 8700G scores 18131 points in the multi-threaded (nT) test and 1826 points in the single-threaded (1T) test.
- Ryzen 5 8600G comes in with 13979 points for the nT test and 1803 points for the 1T test.
In comparison to the Ryzen 5700G:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G sees a 22% improvement in both multi-core and single-core performance, indicating a significant generational leap.
Against the Ryzen 7700:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G is slightly behind by 10% in multi-threaded performance and 6% in single-threaded performance, which might be due to differences in clock speeds, TDP, or architectural enhancements.
CINEBENCH R23 is known for its real-world rendering scenario based on Cinema 4D’s engine, and it’s a reliable tool for assessing a CPU’s performance under prolonged load, especially with the custom stress test feature.
These performance improvements in the 8700G and 8600G are indicative of the advances AMD has made with their new generation of APUs, balancing CPU and GPU performance in a single chip, which could be particularly advantageous for users who seek a capable all-in-one processor for both general computing and moderately demanding graphics tasks.
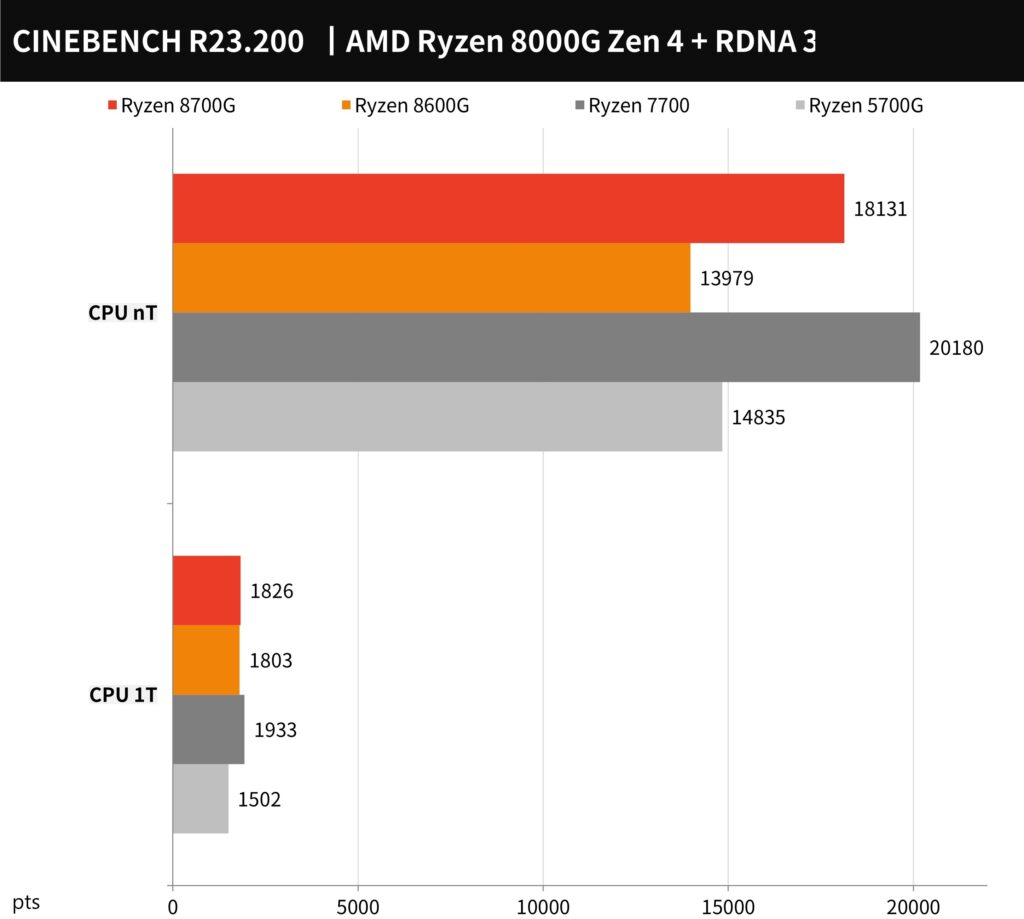
The comparative performance of the AMD Ryzen 8000G series (Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G) alongside the Ryzen 7700 and the Ryzen 5700G. Here’s how the processors stack up in this benchmark:
- Ryzen 7 8700G:
- Multi-threaded (nT) score: 18131 points
- Single-threaded (1T) score: 1826 points
- Ryzen 5 8600G:
- nT score: 13979 points
- 1T score: 1803 points
- Ryzen 7700:
- nT score: 14835 points
- 1T score: 1933 points
- Ryzen 5700G:
- nT score: 20180 points
- 1T score: 1502 points
From this data, we can observe the following:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G performs very competitively in multi-threaded scenarios, coming close to the Ryzen 7700 and outperforming the Ryzen 5 8600G by a significant margin.
- In single-threaded performance, both the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G deliver similar scores, indicating their per-core performance is closely matched.
- Compared to the previous generation Ryzen 5700G, both the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G show substantial improvements, particularly in single-threaded tasks.
- Although the Ryzen 5700G has a higher nT score, it’s worth noting that the newer generation processors are likely to be more efficient due to the improved architecture and manufacturing process.
This benchmark indicates that the Ryzen 8000G series offers a significant leap in performance, especially in terms of single-core operations, which are crucial for tasks that don’t efficiently utilize multiple cores. The data also suggests that these APUs are well-suited for users who require strong performance for both general computing and more demanding applications, such as content creation and gaming.
AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Excel in UL Procyon and PugetBench Tests: Dominating in Photoshop, Lightroom, and DaVinci Resolve Performance
The performance of the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G in UL Procyon Photo Editing Benchmark seems to be quite impressive. The Ryzen 7 8700G scored a total of 7217 points with individual scores of 9251 in image retouching and 5631 in batch processing. The Ryzen 5 8600G, on the other hand, achieved a total score of 6849, with 8946 in image retouching and 5245 in batch processing. This indicates a 31% improvement in overall performance for the 8700G compared to the 5700G, and it’s slightly behind the 7700 by about 5%.
These scores reflect the capability of these processors to handle demanding tasks in photo editing applications like Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom. The Ryzen 7 8700G’s strong performance in particular showcases its suitability for creative workflows that involve both CPU and GPU-intensive tasks.
The performance details and how the APUs fare against other processors in different tasks can be insightful when choosing components for a build focused on photo editing and content creation. For more detailed reviews and benchmarks, sources like HotHardware provide comprehensive insights into the performance of these processors in a variety of scenarios.
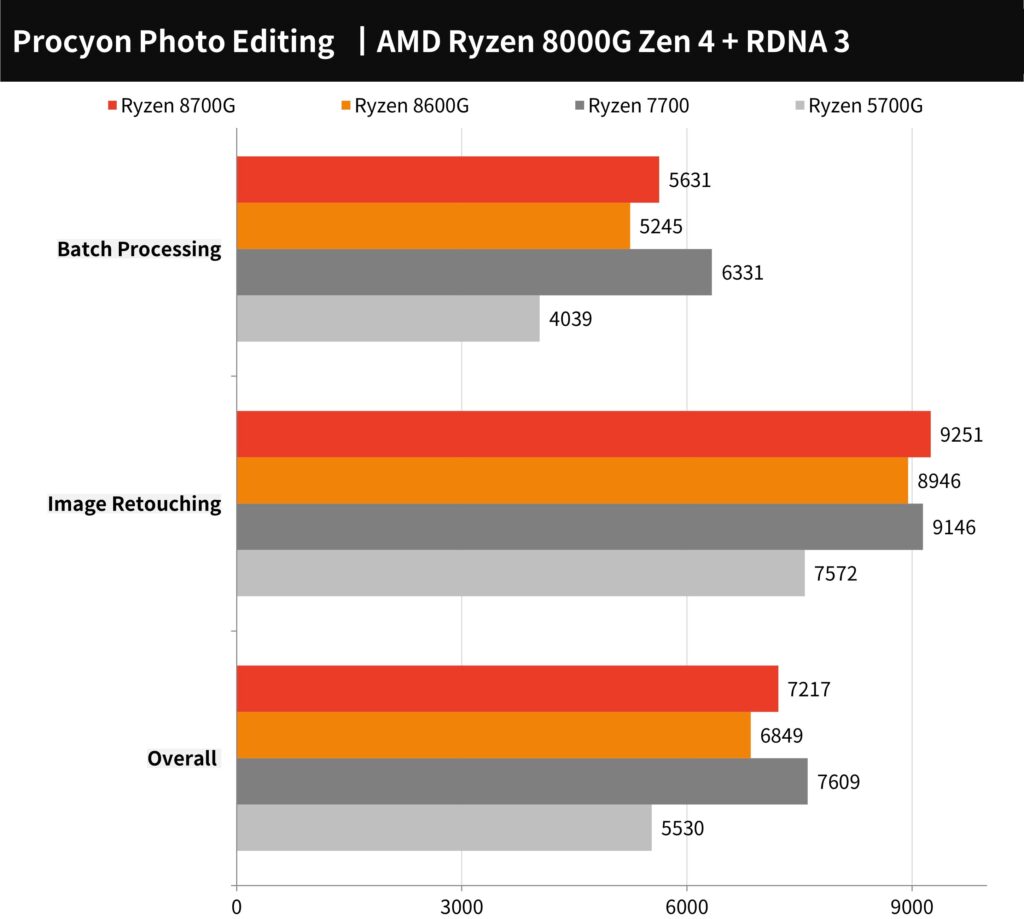
The UL Procyon Photo Editing Benchmark results shown in demonstrate the performance of various AMD processors in tasks related to photo editing using Adobe Photoshop and Lightroom Classic.
Here are the scores from the benchmark:
- The Ryzen 7 8700G leads with an overall score of 7217 points, excelling particularly in the Image Retouching test with a score of 9251 points, and achieving 5631 points in Batch Processing.
- The Ryzen 5 8600G follows with an overall score of 6849 points, scoring 8946 points in Image Retouching and 5245 points in Batch Processing.
- For comparison, the Ryzen 7700 and Ryzen 5700G also have their scores presented, which are lower in both categories.
This chart indicates that the newer Ryzen 7 8700G offers a significant performance improvement in both single-photo editing and batch-processing workflows compared to its predecessors. The higher scores reflect the processors’ ability to handle complex, compute-intensive tasks efficiently, which is crucial for professionals in the field of photo editing and content creation.
The benchmark clearly shows the advancement AMD has made with their latest generation of processors, offering enhanced capabilities for creative workloads that can benefit from both the CPU and GPU performance improvements.
The AMD Ryzen 8700G and 8600G APUs have been showing significant performance gains in both single and multi-thread workloads in various benchmarks, suggesting these are strong contenders for systems without dedicated graphics cards. The performance uplift compared to their 5000-series predecessors is notable, with the Ryzen 7 8700G leading in multi-threaded benchmarks and showing a 20-22% improvement in single-thread performance. These are synthetic benchmarks and real-world performance in applications like gaming may vary. More detailed, real-world performance reviews are expected to provide a clearer picture of these gains.
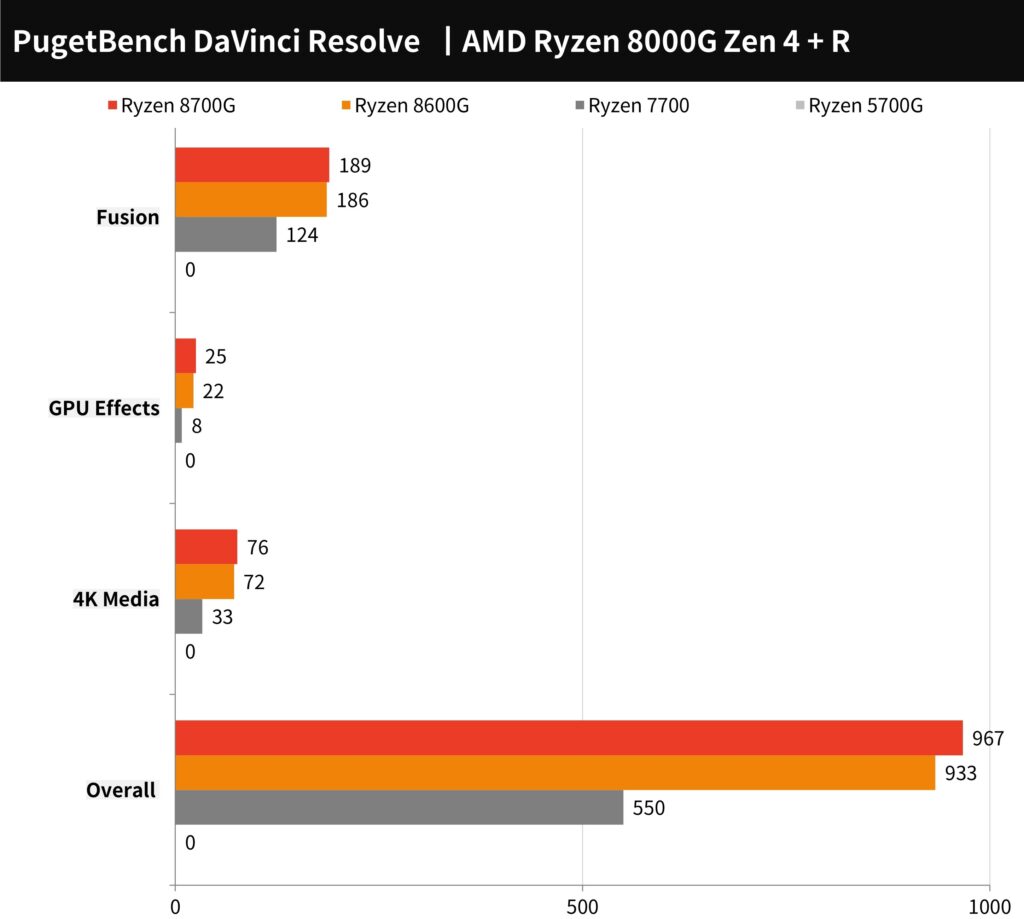
The PugetBench for DaVinci Resolve benchmark chart shows the performance scores for AMD Ryzen 8000G series processors. The Ryzen 7 8700G scores 967 overall, with high marks in the 4K Media, GPU Effects, and Fusion tests. The Ryzen 5 8600G follows closely with an overall score of 933. These scores demonstrate their capabilities in video editing tasks, with the 8700G showing a slight edge over the 8600G, particularly in GPU-accelerated tasks and Fusion composite scores. This benchmark is a useful indicator of the processors’ performance in demanding video editing scenarios.
Analyzing AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G in AIDA64, WinRAR, and 7-Zip: Impressive Memory Bandwidth and Compression Performance Benchmarks
The AIDA64 memory benchmark results for the AMD Ryzen 8700G and 8600G processors using G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo DDR5-6400 RAM demonstrate high memory bandwidth performance, with read speeds around 99129 MB/s and write speeds approximately 75309 MB/s. The memory latency for both processors is relatively low, at 66.3ns and 67.6ns, respectively. These results indicate that both processors can effectively utilize the high-speed DDR5 memory, providing fast data transfer rates that are beneficial for memory-intensive applications.
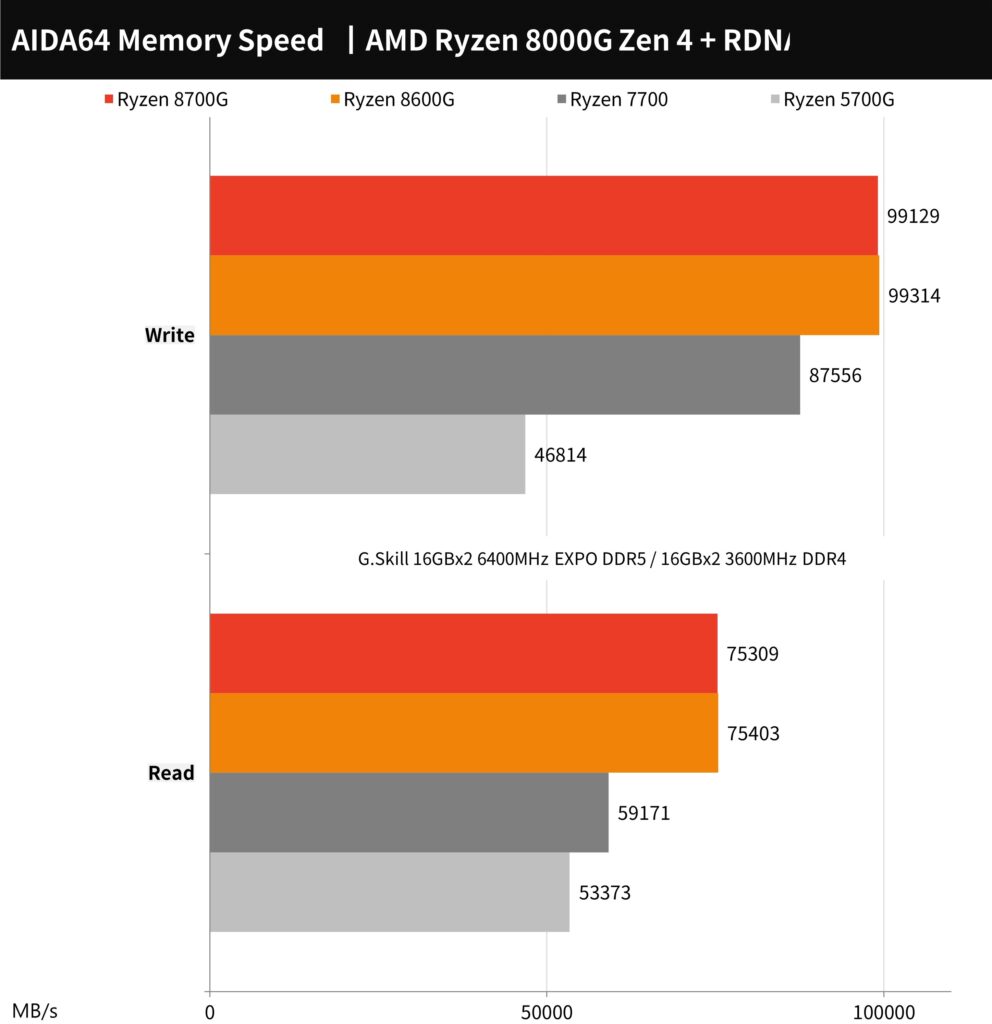
The AIDA64 memory benchmark chart shows the performance of AMD Ryzen processors with the Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G using G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo DDR5-6400 memory. The 8700G and 8600G exhibit nearly identical read speeds, close to 99 GB/s, and write speeds around 75 GB/s. These results highlight the capabilities of DDR5 memory in conjunction with AMD’s latest CPUs, offering high bandwidth, which is beneficial for tasks that require quick memory access. The chart serves as a good reference for understanding the memory performance one can expect from these setups.
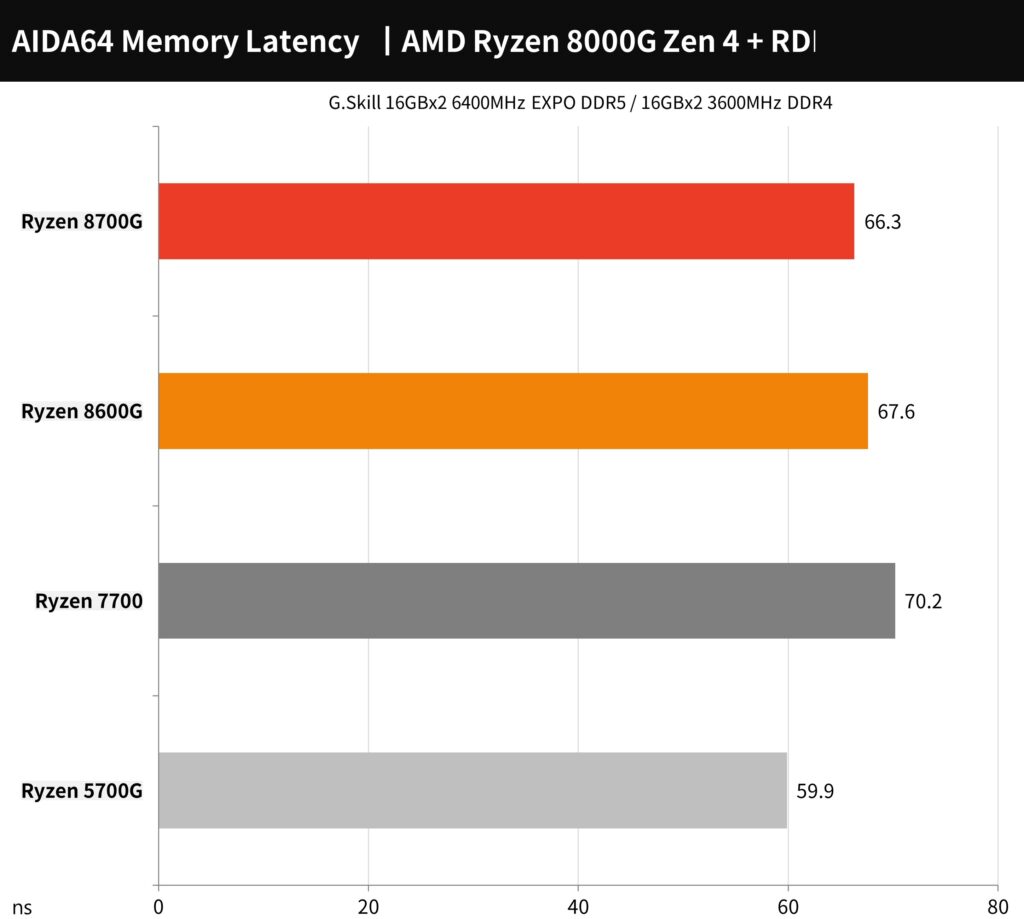
The AIDA64 Memory Latency chart displays the latency results for the AMD Ryzen 8000G series processors. The Ryzen 7 8700G has a latency of 66.3ns, while the Ryzen 5 8600G is slightly higher at 67.6ns. These results indicate tight and responsive memory performance, with lower latency being better for quick memory operations. The Ryzen 7700 and the older 5700G are also included for comparison. The chart showcases the advancements in memory optimization for the newer Ryzen series.
In a WinRAR compression performance test, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G achieved a rate of 29523 KB/s, while the Ryzen 5 8600G recorded a performance of 23468 KB/s. Compared to the Ryzen 5700G, the 8700G shows a 14% improvement in performance. However, it is outperformed by the Ryzen 7700, which has a 28% higher performance rate in the same test. This suggests that while the 8700G offers advancements over its predecessor, there is still a gap when compared to some other contemporary processors in compression tasks.
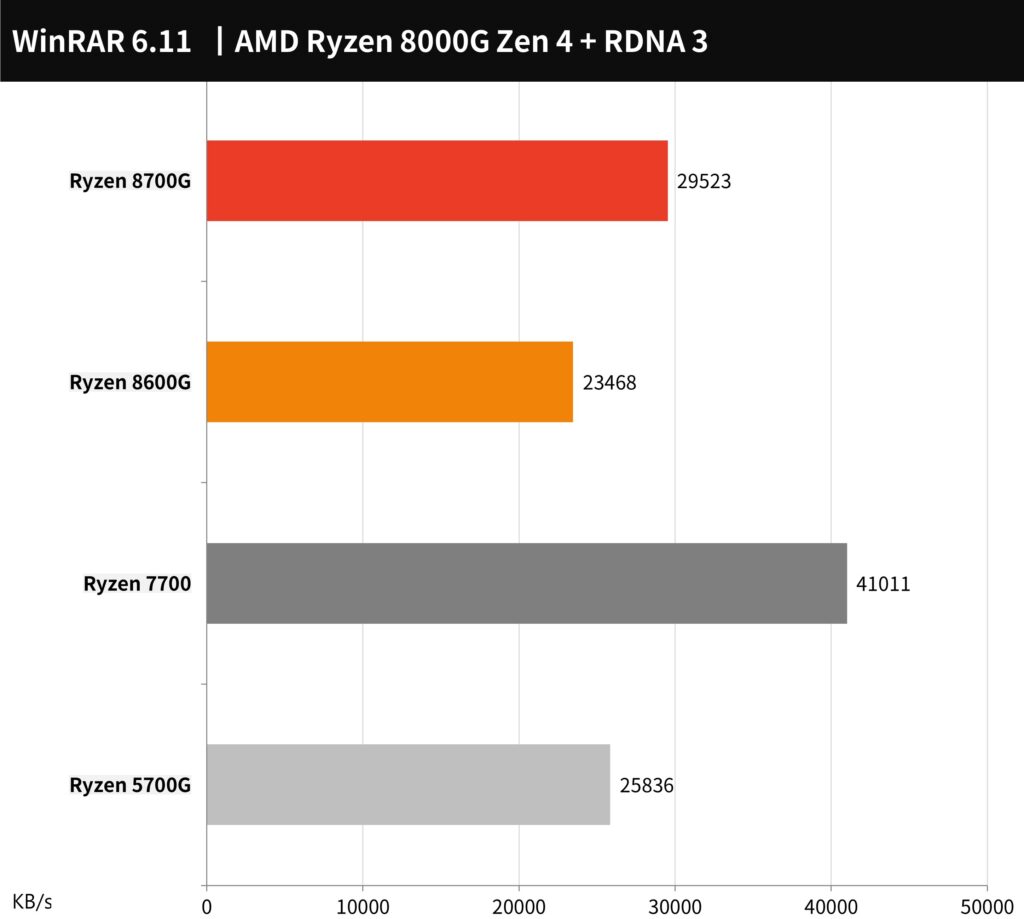
The WinRAR benchmark chart provided shows the compression performance of different AMD Ryzen processors, with the Ryzen 7 8700G achieving 29523 KB/s. This score represents a significant improvement over the previous generation Ryzen 5 700G and competes closely with the Ryzen 7700, which shows a higher performance at 41011 KB/s. The Ryzen 5 8600G also demonstrates strong performance with a score of 23468 KB/s. This chart illustrates the processors’ capabilities in handling file compression tasks, which are common in many computing workflows.
In 7-Zip benchmark testing, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G has shown impressive performance, reaching 113.171 / 126.488 GIPS, while the Ryzen 5 8600G also delivers strong performance with scores of 88.666 / 97.362 GIPS. These results indicate that both processors are very capable of leveraging their multi-core architectures to efficiently handle demanding compression tasks, a key strength of the 7-Zip software which is designed to utilize multi-core processing to its full extent.
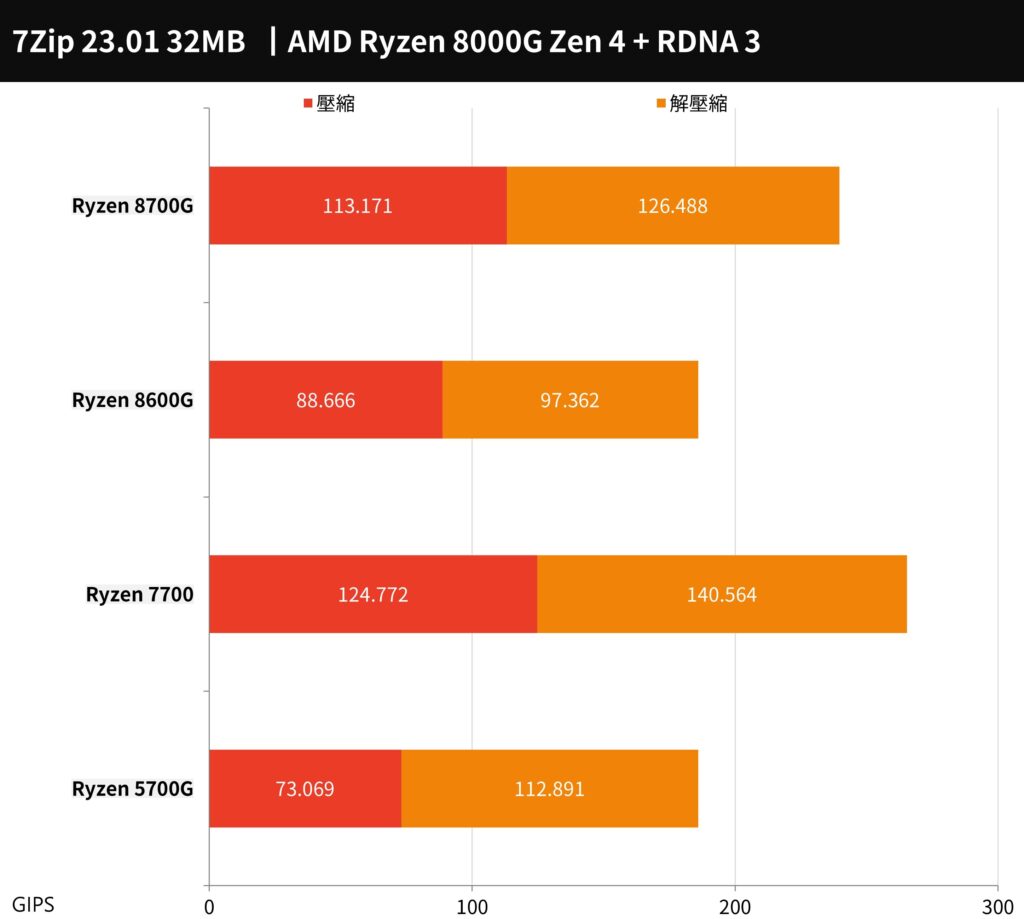
The 7-Zip benchmark chart shows the performance of AMD Ryzen processors in GIPS (Giga Instructions Per Second). The Ryzen 7 8700G scores 113.171 GIPS in single-threaded and 126.488 GIPS in multi-threaded performance, while the Ryzen 5 8600G achieves 88.666 GIPS and 97.362 GIPS, respectively. These results indicate that the 8700G offers superior performance in both single and multi-threaded tasks within 7-Zip, a tool that benefits from multi-core capabilities. The Ryzen 7700 and 5700G are included for comparison, with the 7700 outperforming the 8700G in this benchmark.
AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Shine in PCMark 10: Superior Performance in Essentials, Productivity, and Digital Creation Compared to Predecessors
The PCMark 10 scores indicate that the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G achieved a total score of 8012, while the Ryzen 5 8600G scored slightly lower at 7756. These tests cover a variety of computer tasks ranging from basic operations like app startup speeds, video conferencing, and web browsing in the Essentials category, to productivity tasks involving spreadsheets and document editing, as well as digital content creation with photo and video editing, rendering, and visualization. The 8700G’s superior performance, especially in GPU-accelerated tasks, explains its edge over the 7700, marking an approximate 11% increase in overall computer performance compared to both the 5700G and the 7700.
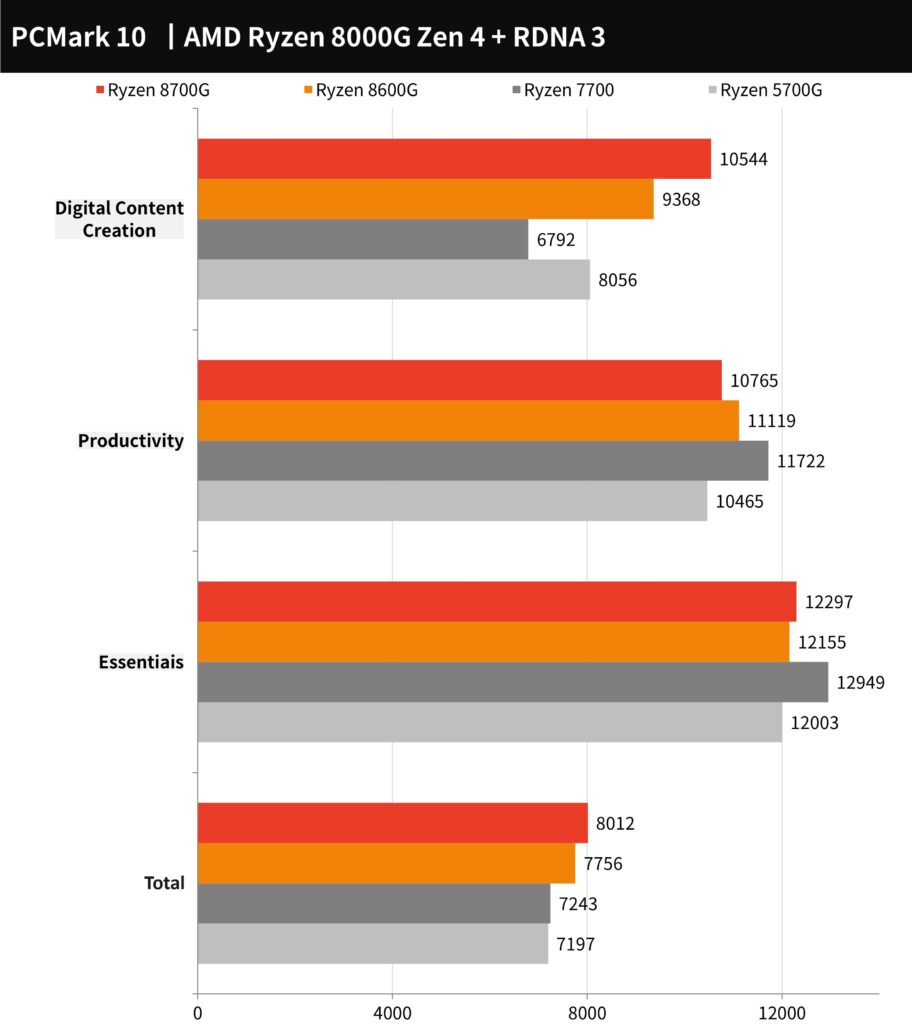
The PCMark 10 benchmark chart shared indicates that the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G scores highly across all categories, excelling particularly in Digital Content Creation. The Ryzen 5 8600G follows closely behind, showcasing that both CPUs are well-suited for a range of tasks from basic computing to more demanding productivity and content creation tasks. The Ryzen 7700 and 5700G are included for comparison, showing where the 8700G and 8600G stand against these other processors. Overall, the 8700G and 8600G demonstrate strong performance in the PCMark 10 benchmark, indicative of their capabilities in everyday computing and intensive workloads.
The PCMark 10 Applications benchmark focuses on productivity tasks using Microsoft Office software like Word, Excel, PowerPoint, and Edge. It primarily tests the performance of the CPU and RAM. In this benchmark, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G scored 15382 points and the Ryzen 5 8600G scored 14596 points. The Ryzen 7 8700G exhibits a 9% performance improvement over the Ryzen 5 700G and trails the Ryzen 7700 by 9%. This indicates that the 8700G is very capable of office productivity tasks, offering improvements over the previous generation while slightly behind the 7700 in such applications.
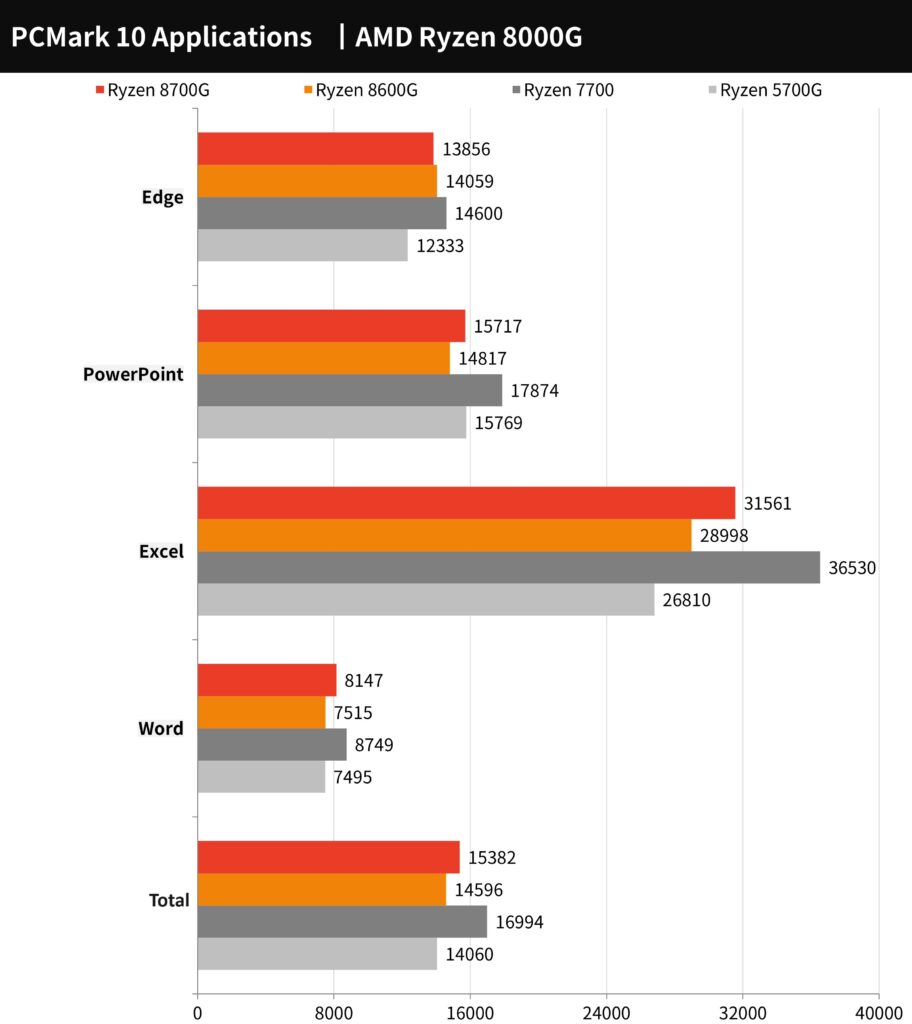
The PCMark 10 Applications benchmark chart shows how the AMD Ryzen 8000G series processors perform productivity tasks using Microsoft Office applications. The Ryzen 7 8700G achieves the highest scores, particularly in the Excel and PowerPoint portions, suggesting strong performance in data analysis and presentation software. The Ryzen 5 8600G also scores well, indicating it’s a capable processor for office productivity tasks. The chart demonstrates the processors’ effectiveness in handling everyday productivity tasks that professionals frequently encounter.
AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Excel in 3DMark Gaming Benchmarks: Outclassing 5700G and Intel i7-14700K in Fire Strike and Time Spy
In 3DMark benchmark tests, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G have delivered impressive results. In the Fire Strike Graphics test, which measures DirectX 11 performance, the 8700G scored 9709 points, and the 8600G scored 8060 points. These scores represent more than double the performance improvement over the Ryzen 5700G and a substantial lead over the i7-14700K’s integrated graphics.
In the Time Spy Graphics test, focusing on DirectX 12 performance, the 8700G scored 3313 points, while the 8600G scored 2897 points. The performance of the 8700G is notably higher than the 5700G and significantly outpaces the i7-14700K’s integrated graphics, showcasing the robust graphical capabilities of the Ryzen 8000G series APUs.
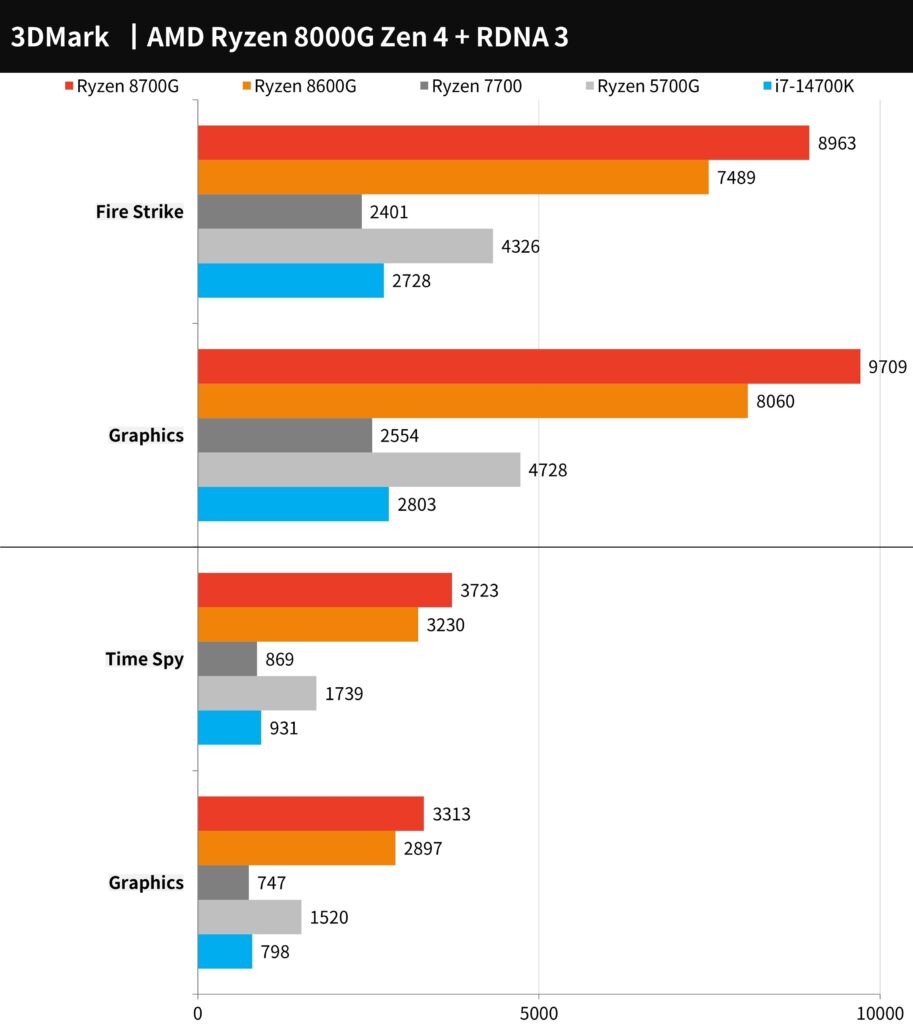
The 3DMark benchmark chart shared highlights the scores for AMD Ryzen 8000G series processors in graphical performance tests. The Ryzen 7 8700G shows a strong lead in both Fire Strike and Time Spy tests, indicating robust gaming and graphical capabilities, particularly in comparison to the integrated graphics of the i7-14700K. This performance is a testament to the significant improvements AMD has implemented in their RDNA 3 integrated GPUs, confirming these APUs as a competitive option for gaming and graphics-intensive applications without the need for discrete graphics cards.
In the 3DMark CPU tests that measure physical computation and simulation tasks across varying thread counts, the AMD Ryzen 8700G shows a performance difference of around 9% compared to the Ryzen 5700G. The Ryzen 5 8600G, having fewer cores, doesn’t perform as well as the 5700G in tasks that utilize 8 threads, which is a sweet spot for many modern DirectX 12 games. Older games typically prefer fewer threads. Naturally, CPUs like the Ryzen 7700 and Intel i7-14700K, which likely have higher core and thread counts, achieve better scores in these CPU-intensive tests.
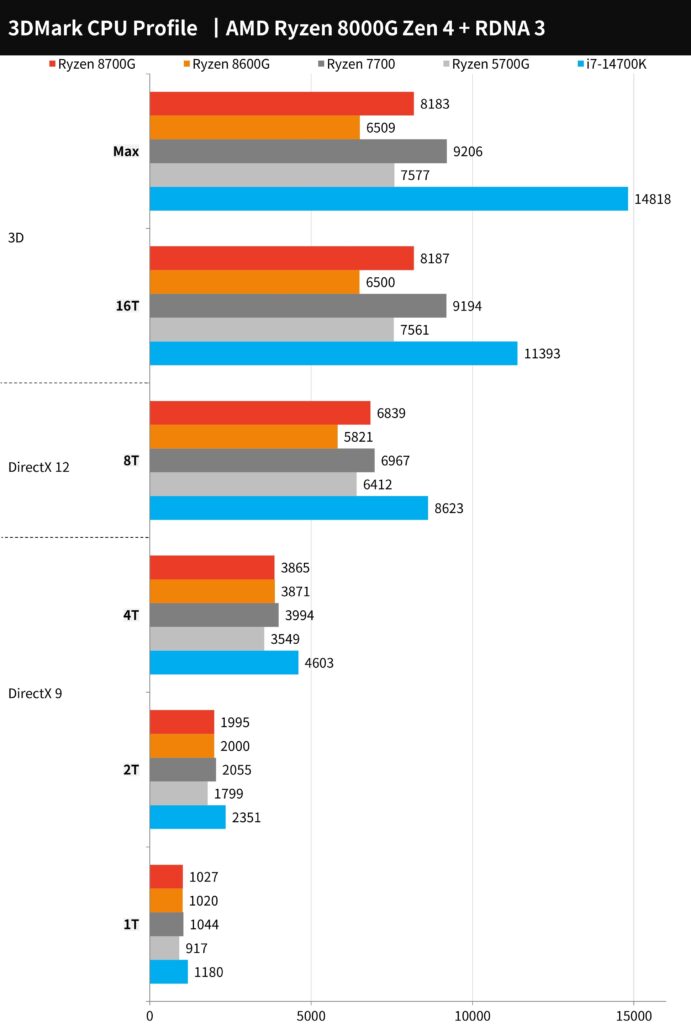
The 3DMark CPU Profile chart indicates the performance of AMD Ryzen 8000G series processors across different thread counts, relevant for various tasks from gaming to 3D rendering. The Ryzen 7 8700G shows strong performance across all thread counts, excelling particularly in the more demanding tests that simulate modern DirectX 12 gaming preferences and 3D rendering tasks that utilize 16 or more threads. The Ryzen 5 8600G follows closely, with performance reflective of its core and thread count, especially in tasks optimized for fewer threads. The chart demonstrates the CPUs’ capabilities in handling complex computing tasks and their suitability for gaming and content creation.
AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Gaming Prowess Tested: Dominating AAA and eSports Titles at 1080p with High FPS Scores
In gaming performance tests for nine AAA titles at 1080p resolution with low settings, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G achieved an average of 78.4 FPS, while the Ryzen 5 8600G averaged 68.3 FPS. Most games performed well above 60 FPS, except “Avatar: Frontiers of Pandora.” The 8700G showed a significant performance increase over both the Ryzen 5700G and the i7-14700K. In esports titles like “Counter-Strike 2” and “Tom Clancy’s Rainbow Six: Siege,” the 8700G and 8600G also delivered high FPS, showcasing the benefits of CPU performance and clock speed improvements in competitive gaming scenarios.
Stress Test Insights: AMD Ryzen 8700G & 8600G Under the Microscope for Temperature and Power Efficiency
In the stress tests using a 280mm AIO cooling system at full fan and pump speeds, the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G maintained a temperature of 55.3°C at 4.96GHz across all cores during the AIDA64 CPU stress test. The Ryzen 5 8600G was slightly cooler at 50.5°C at 4.78GHz. Under the more intense FPU test, which simulates maximum load and power consumption conditions, temperatures rose to 93.5°C for the 8700G and 90.3°C for the 8600G. These tests demonstrate the thermal performance of these CPUs under various stress conditions.
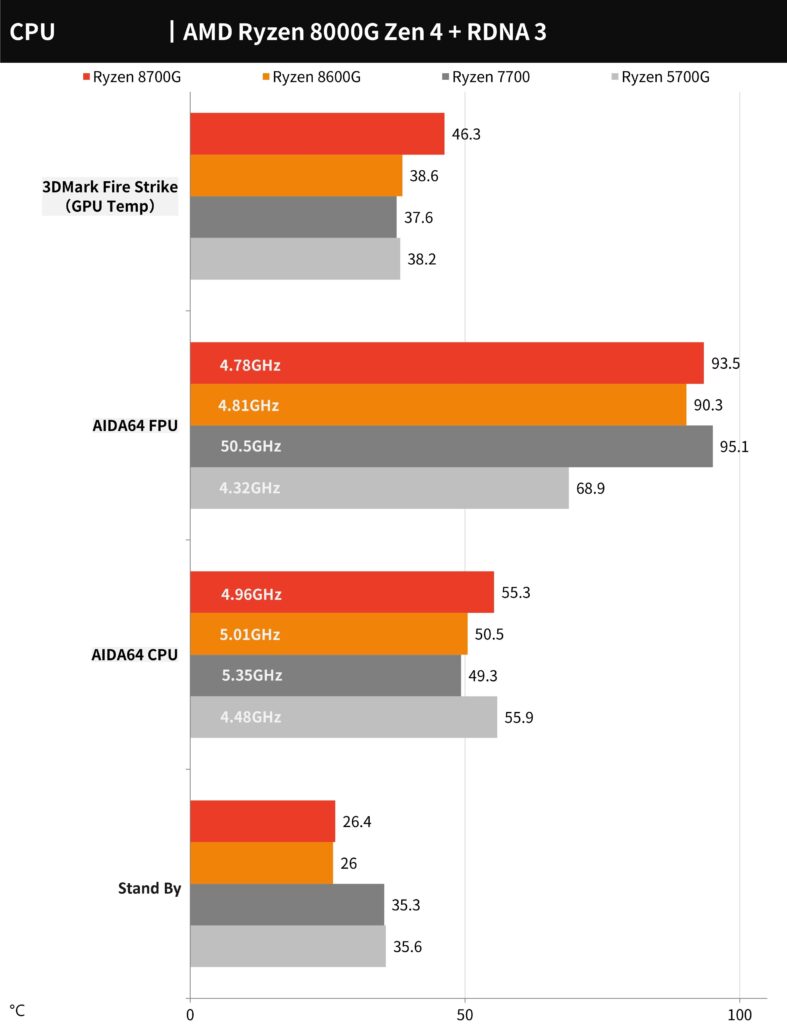
The CPU temperature test chart indicates that both the AMD Ryzen 7 8700G and Ryzen 5 8600G maintain reasonable temperatures under various stress conditions, with the AIDA64 CPU test showing temperatures just over 50°C for both CPUs. Under the more demanding AIDA64 FPU test, temperatures approach the higher end but remain within operational limits. These results are a good indication of the thermal performance and cooling efficiency of the respective CPUs when paired with a 280mm AIO cooling solution.
The power consumption metrics for the AMD Ryzen 8700G and 8600G CPUs indicate that under maximum load, the 8700G can reach up to 124.1 watts, with a gaming average around 87 watts. The 8600G has a slightly lower maximum power consumption at 98.2 watts, and during gaming, it averages 66.1 watts. These figures provide insights into the power efficiency of these processors during intensive tasks and gaming scenarios.
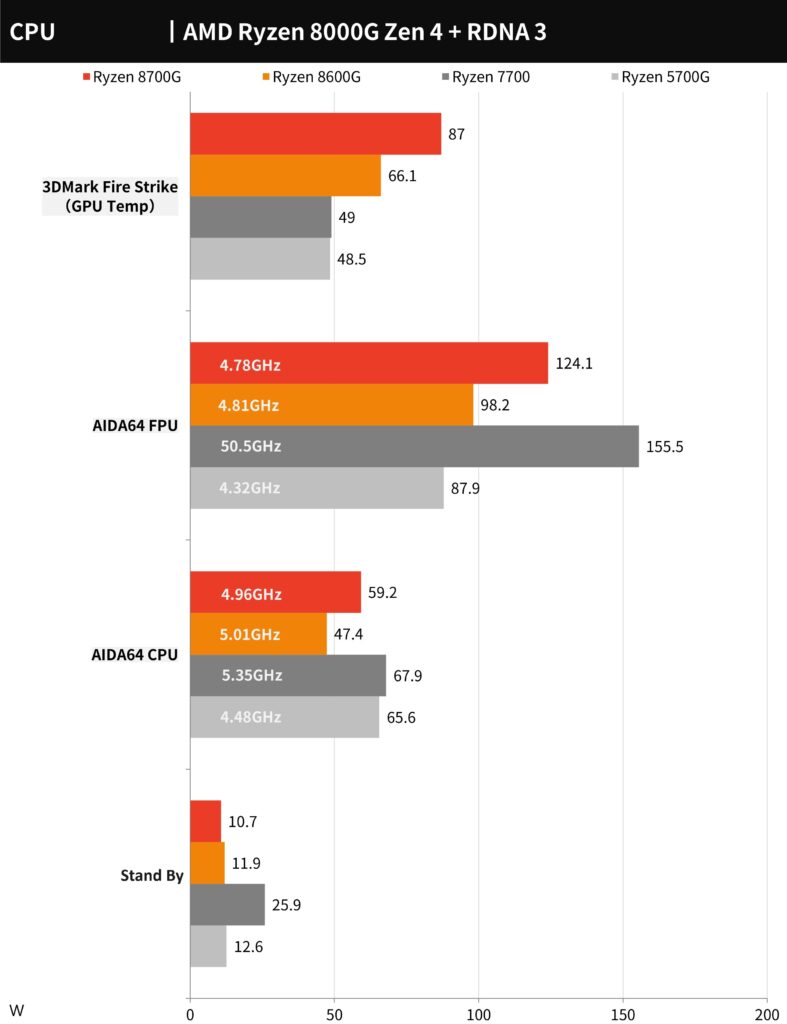
The CPU power consumption test chart illustrates the power efficiency of the AMD Ryzen 8000G series during various tasks. The Ryzen 7 8700G peaks at 124.1 watts under maximum load and settles around 87 watts during gaming. The Ryzen 5 8600G shows lower consumption with a peak of 98.2 watts and approximately 66.1 watts during gaming. These figures reflect the processors’ energy demands during intensive operations and typical gaming conditions, indicating good efficiency for high-performance CPUs.
Summarize
The AMD Ryzen 7 8700G is highlighted as the strongest integrated graphics processor currently on the PC platform, able to deliver an average of 78.4 FPS at 1080p resolution with low graphical settings. The Ryzen 5 8600G also performs well, averaging 68.3 FPS. When compared to the previous generation Ryzen 5700G, the 8700G and 8600G show significant gaming performance improvements, thanks to their RDNA 3 architecture-based Radeon 780M and 760M graphics. Although they slightly trail behind their core-equivalent Ryzen 7700 and 7600 in terms of processor performance, their competitive pricing makes them a solid choice for entry-level gamers. With a complete system build, including CPU, motherboard, RAM, case, and power supply, costs can be kept under 25,000 TWD. For enhanced gaming performance, it is recommended to enable FSR acceleration if available or use AMD Software: Adrenalin Edition 24.1.1 to activate AMD Fluid Motion Frames for stable entry-level gaming performance.
If this article is helpful for you, please share this article with your friends on social media. Thank you!
This article is based on the personality of the reviews. You are responsible for fact-checking if the contents are not facts or accurate.
Title: AMD Ryzen 7 8700G Review: Unleashing the Power of PC’s Best APU with Zen 4 and RDNA 3 Cores for Ultimate Gaming at 1080p