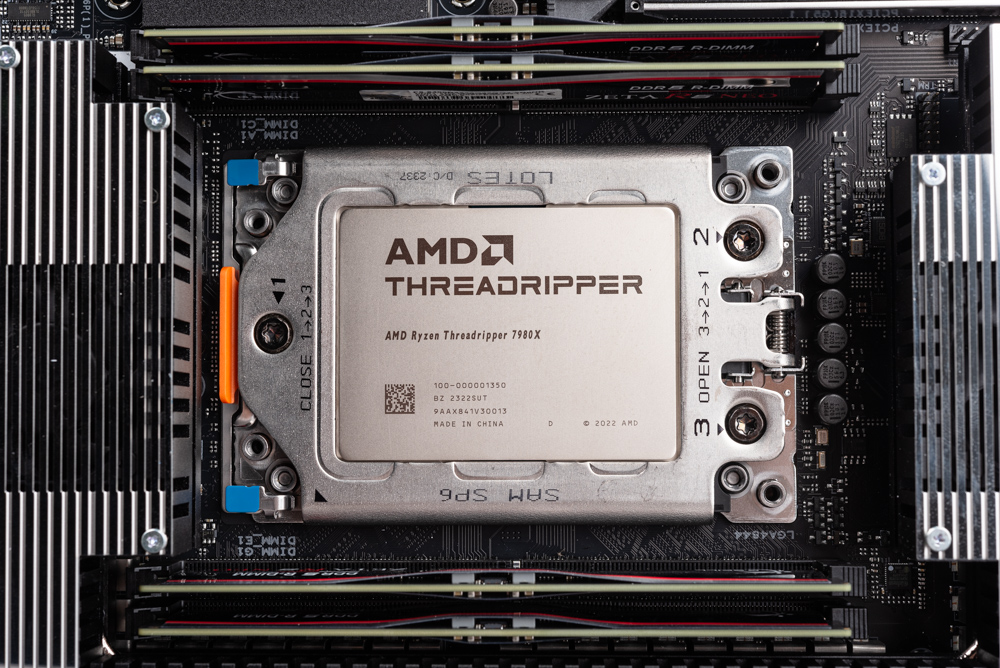

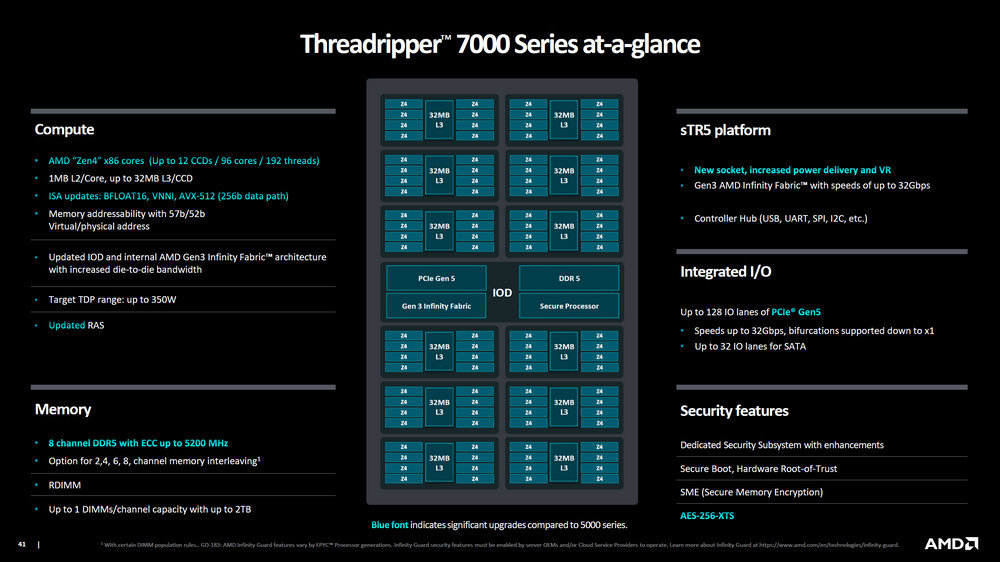
The High-End Desktop (HEDT) platform, which had been awaiting updates for an extended period, has made a remarkable comeback. AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, featuring powerhouse processors like the 7980X, boasts an impressive configuration of up to 64 cores and 128 threads. The series also includes the 7970X, which offers 32 cores and 64 threads, and the 7960X, equipped with 24 cores and 48 threads. Accompanying these processors is the exclusive TRX50 chipset, which enhances the system’s capabilities with features like 4 Channel 1TB DDR5 RDIMM memory support and 92 PCIe lanes. It offers PBO overclocking capabilities. This combination of advanced features addresses the demanding needs of high-end users and content creators, particularly in terms of multi-core performance, high-capacity memory, and extensive PCIe expansion options.
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 Series HEDT Processors
While the mainstream Ryzen 7950X, featuring a 16C32T core count, dual-channel DDR5 with a maximum memory capacity of 192GB, and robust single-card GPU performance, has garnered significant attention, it seems that the flagship High-End Desktop (HEDT) platform is gradually being overshadowed in the gaming community. However, there remains a niche segment of users who rely heavily on the HEDT platform for professional applications. These include AI training, 3D rendering, VFX simulation, and the physical simulation processes in design and manufacturing. For such demanding tasks, users require processors with a higher core count, expansive memory capacity, and the capability for multi-GPU expansion.
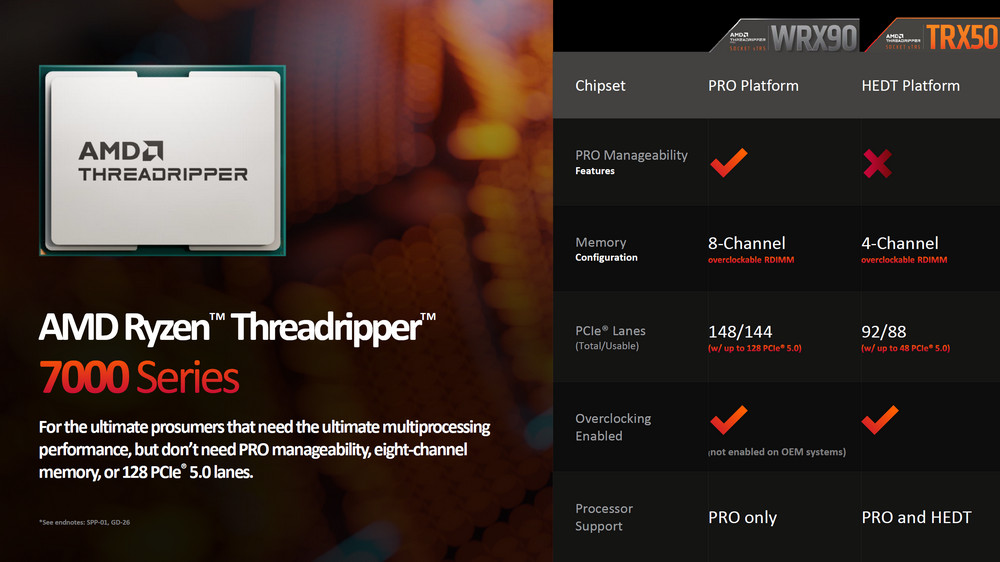
In response to these varied needs, AMD has strategically positioned its product lines. The EPYC series continues to be AMD’s primary offering for server solutions. For workstations, AMD introduces the Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7000 WX-S series, targeting OEMs, system integrators (SIs), and other professional clientele. For the retail market, AMD provides the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, accompanied by the TRX50 chipset, catering to those seeking high-performance computing solutions outside of a professional setting. This strategic differentiation ensures that AMD addresses the diverse requirements of both professional and mainstream markets.

The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, a high-end offering in the consumer market, does not incorporate the AMD Pro commercial features. Utilizing the same sTR5 socket and fabricated using TSMC’s advanced 5nm FinFET process, this series showcases impressive technical specifications.
Leading the lineup is the 7980X, a powerhouse processor equipped with the highest core count in the series: 64 cores and 128 threads. It boasts a substantial 5.1GHz Boost clock and a large 256MB L3 cache, making it an ideal choice for tasks that demand extensive multi-threading capabilities.
The 7970X, another prominent model in this series, offers a balanced blend of performance and efficiency. It features 32 cores and 64 threads, complemented by a slightly higher 5.4GHz Boost clock and a 128MB L3 cache. This configuration makes it well-suited for applications that require a mix of high core count and fast clock speeds.
Finally, the 7960X caters to those who need a robust but slightly less extreme option. It is configured with 24 cores and 48 threads, a 5.3GHz Boost clock, and a 128MB L3 cache. This model is particularly adept at handling demanding applications that require a significant amount of processing power but may not necessarily need the extreme core counts of its higher-end counterparts.
In summary, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, with its varied configurations, is designed to meet the high-performance computing needs of a wide range of users, from enthusiasts to professionals in fields like content creation, 3D rendering, and other compute-intensive tasks.

The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series processors, encompassing the 7980X, 7970X, and 7960X models, uniformly support 4-channel DDR5 RDIMM memory, a substantial feature that contributes to their high-performance capabilities. All three processors are equipped with 48 PCIe 5.0 lanes, offering extensive bandwidth and compatibility with the latest high-speed peripherals and components. These processors also share a Thermal Design Power (TDP) specification of 350 watts, indicative of their high performance and power consumption characteristics.
A significant advancement in this new generation of Ryzen Threadripper processors is observed in their single-thread Boost clock performance. This improvement narrows the gap between the Threadripper 7000 series and the mainstream Ryzen 7950X in terms of single-thread performance. This enhancement is particularly notable, as it marks a considerable leap over the previous generation of Threadripper processors, making the Threadripper 7000 series more competitive in applications that benefit from high single-thread performance.
However, it’s important to note the cost implications associated with using DDR5 RDIMM memory in these processors. The adoption of DDR5 memory, while offering higher bandwidth and improved performance, also leads to a higher construction cost for the relative platform. This cost factor is a critical consideration for users who are evaluating the Threadripper 7000 series for their high-end computing needs, particularly in comparison to more cost-effective alternatives that may offer slightly less performance but at a significantly lower price point.
Overall, the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series stands out for its advanced features and high performance, suitable for users who require exceptional multi-threading capabilities and are willing to invest in a premium computing platform.
TRX50 chipset: DDR5 RDIMM, 92 PCIe lanes, supports Pro processor
The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, paired with the exclusive TRX50 chipset, presents a high-end platform designed primarily for consumer and enthusiast markets, distinctively not supporting AMD Pro commercial features. This delineation focuses the TRX50 chipset and the Threadripper 7000 series on high-performance and overclocking capabilities rather than enterprise-oriented functionalities.
Key features of the TRX50 chipset include:
- Support for 4-Channel Overclocked RDIMM Memory: This allows for enhanced memory performance, particularly beneficial for applications that demand high memory bandwidth and capacity. Overclocking capabilities further enhance this performance, making it a suitable choice for users who need to push the limits of their system’s memory.
- Total of 92 PCIe Lanes (88 Available): This extensive PCIe lane support, including 48 lanes of the latest PCIe 5.0 standard, provides substantial bandwidth for multiple high-speed peripherals and components. The availability of 88 lanes for use ensures that users can integrate various components, such as multiple GPUs, NVMe storage devices, and other PCIe-based hardware, without bandwidth limitations.
- Processor Overclocking Functions: The TRX50 chipset complements the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series processors by supporting advanced overclocking. This feature allows enthusiasts and professionals to maximize the performance of their processors beyond the factory-set specifications, offering potential gains in compute-intensive tasks like rendering, simulation, and content creation.
- Compatibility with Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7000 WX-S Processors: In addition to supporting the standard Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, the TRX50 chipset is also compatible with the Ryzen Threadripper PRO 7000 WX-S series. This versatility provides users with the flexibility to choose between the consumer-oriented Threadripper 7000 series and the more workstation-focused Threadripper PRO 7000 WX-S series based on their specific needs and requirements.
The combination of these features makes the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series with the TRX50 chipset a compelling choice for users seeking top-tier performance in tasks that benefit from high core counts, extensive memory bandwidth, and expansive PCIe connectivity. This platform is particularly well-suited for high-end gaming, content creation, 3D rendering, and other professional applications that require exceptional computational power.
For the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, memory selection and heat dissipation are critical aspects to consider for optimal performance:
- Memory Selection – DDR5 RDIMM: The Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series mandates the use of DDR5 RDIMM (Registered DIMM) memory. This type of memory is known for its reliability and stability in high-performance computing environments, making it an ideal choice for the demands of the Threadripper 7000 processors. DDR5 RDIMM offers higher bandwidth and greater capacity compared to previous generations, which is essential for memory-intensive tasks such as video editing, 3D rendering, and scientific simulations.
- EXPO Overclocking Memory Support: The platform supports EXPO (EXtended Profiles for Overclocking) memory, AMD’s answer to Intel’s XMP. EXPO allows for straightforward overclocking of DDR5 memory, providing an easy way to enhance memory speed and performance beyond standard specifications. This feature is particularly beneficial for users who require extra performance for their applications.
- Initial Memory Detection Time: Users should be aware that the first boot-up of the platform may take longer than usual, potentially extending over several minutes. This delay is primarily due to the system’s process of detecting and configuring the DDR5 RDIMM memory. While this may be slightly inconvenient, it’s a one-time process that ensures optimal memory setup and stability.
- Heat Dissipation – Asetek AIO Water Cooling: To manage the substantial heat output of the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 processors, especially when overclocked, the platform also includes support for Asetek AIO (All-In-One) water cooling solutions. These AIO coolers are specifically designed to handle the high thermal design power (TDP) of the Threadripper series, providing efficient cooling to maintain stable operation and prevent thermal throttling during heavy workloads. The incorporation of a high-capacity Asetek AIO water cooler is a crucial factor for users looking to achieve and sustain peak performance from their Threadripper 7000 series processor.
In summary, the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series requires careful consideration of memory and cooling solutions to harness its full potential. Choosing the right DDR5 RDIMM memory, understanding the initial setup time, and implementing an effective cooling solution like the Asetek AIO water cooler is key to ensuring a stable and high-performing computing environment.


The compatibility and effectiveness of water cooling solutions for the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, particularly the HEDT (High-End Desktop) models, depend significantly on the specific processor and its configuration:
- Water Block Contact Area: The actual area of the water block that makes contact with the CPU’s Integrated Heat Spreader (IHS) is a crucial factor in cooling efficiency. This area needs to be adequately sized and designed to cover the critical heat-generating parts of the processor.
- Compatibility with Up to 8 CCDs (Core Complex Dies): The Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series HEDT models utilize up to 8 CCDs. The size and layout of these CCDs are key determinants of the heat distribution on the processor’s surface. The Asetek AIO water cooling solutions are compatible with this configuration, as their water block is designed to cover and effectively cool this specific arrangement.
- Specific Consideration for 7995WX: For the higher-end model like the 7995WX, which might have different or more extensive cooling requirements due to its potentially higher core count and power consumption, a dedicated radiator may be necessary. This implies that the standard Asetek AIO water cooling solution might not be sufficient for the 7995WX, and users would need to opt for a specialized cooling system. These dedicated radiators are typically larger or have more advanced cooling capabilities to handle the increased thermal output.
In essence, while the existing Asetek AIO water cooling solutions are suitable for the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series with up to 8 CCDs, users with the top-tier 7995WX model may need to invest in more robust cooling systems. This consideration is crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity of the processor, especially under heavy workloads or during overclocking scenarios. Ensuring proper heat dissipation is key to leveraging the full capabilities of these high-performance CPUs.

The power supply requirements for the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, especially considering its high-performance capabilities and potential overclocking scenarios, are indeed substantial:
- Minimum Power Supply Recommendation: For standard operation, it is recommended to use at least a 1000W power supply. This recommendation takes into account the high power consumption of the Threadripper processors, especially given their high core counts and advanced features. A 1000W power supply ensures that there is enough headroom to accommodate the CPU’s power demands along with other components in the system, such as GPUs, storage devices, and cooling systems.
- Power Supply for Overclocking: If you plan to engage in PBO (Precision Boost Overdrive) or manual overclocking, the power requirements increase significantly. In these cases, it is recommended to use a 1600W power supply. Overclocking can substantially raise the power consumption of the processor as it operates beyond its standard specifications. A 1600W power supply provides the necessary power stability and headroom to ensure that the system remains stable and efficient during overclocked operation. This is particularly important to prevent power-related issues that can lead to system instability or hardware damage.
- Considerations for System Stability and Efficiency: Choosing a high-quality power supply unit (PSU) is critical, not just in terms of wattage but also regarding its efficiency rating and reliability. PSUs with high-efficiency ratings (like 80 Plus Gold, Platinum, or Titanium) are preferable as they ensure better power delivery and can help reduce electricity consumption. These high-quality PSUs often come with better voltage regulation and protection features, which are vital for protecting high-end components like the Threadripper CPUs from power surges or fluctuations.
In summary, for users of the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series, especially those engaging in overclocking, selecting the appropriate power supply is a key component of system planning. A 1000W PSU is suitable for standard configurations, while a 1600W PSU is advisable for overclocked systems, ensuring both stable operation and longevity of the components. It’s also crucial to focus on the quality and efficiency of the PSU for the best performance and system reliability.
Media version combination ASUS TRX50, NZXT Kraken 360, DDR5 RDIMM unboxing
For the performance unlock test, AMD’s Ryzen Threadripper 7980X and 7970X processors offer robust capabilities. The 7980X, a high-end model with 64 cores and 128 threads, is designed for intense multitasking and parallel processing. It features a base clock speed of 3.2 GHz and a boost up to 5.1 GHz, a 256MB L3 cache, quad-channel memory support, 48 lanes of PCIe Gen5, and substantial overclocking capabilities, retailing just under $5,000. On the other hand, the 7970X, with 32 cores and 64 threads, strikes a balance between performance and energy efficiency, reaching a max boost clock of 5.3 GHz and necessitating robust cooling for its 350W TDP.
Supporting these processors is the ASUS Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI motherboard, featuring a 36-phase VRM and compatibility with AMD’s SP6 socket. It supports up to 1 TB of ECC R-DIMM DDR5 memory, has a robust power and thermal design, and offers ultrafast connectivity with PCIe 5.0 slots and 10 Gb & 2.5 Gb LAN ports. It offers server-grade IPMI remote management and trusted stability for extensive compatibility.
The NZXT Kraken 360 water cooling radiator, ideal for handling the thermal requirements of these processors, ensures efficient cooling. In testing environments, with the NZXT Kraken AIO cooler, water temperatures stayed below 32°C at idle and under 50°C when fully loaded.
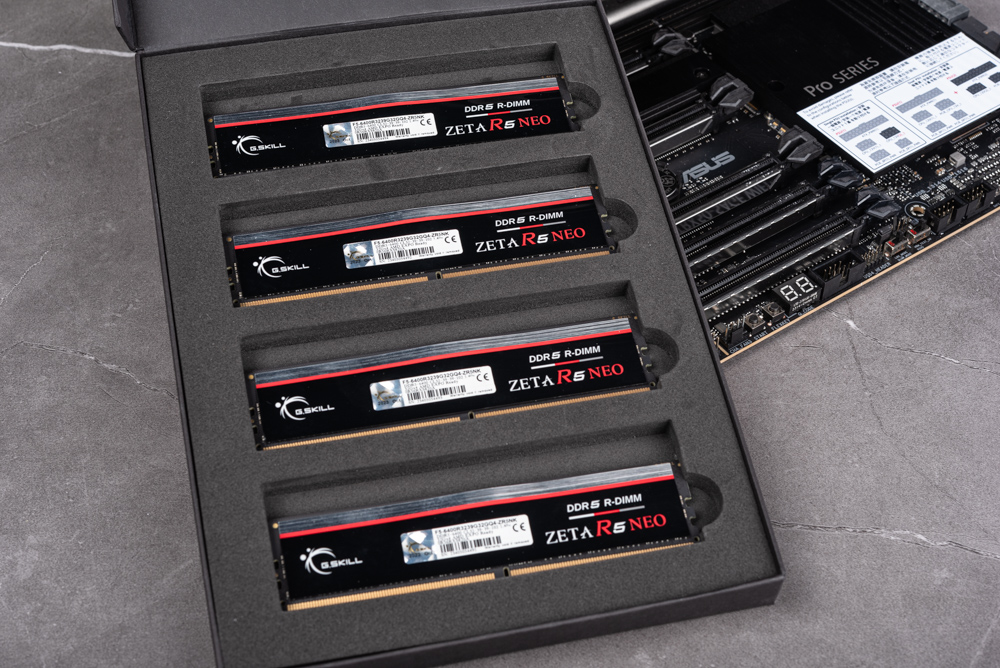
Complementing this setup is G.Skill’s Zeta R5 Neo series, featuring overclocked DDR5 R-DIMM memory kits optimized for the AMD TRX50 chipset and AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series. These kits support AMD EXPO memory overclocking profiles, offering enhanced memory performance tuning, and are available in configurations of up to 128GB (32GBx4) with a speed of DDR5-6400.
The power supply for this system, the CORSAIR HX1500i, is a high-capacity unit rated as Platinum in the 80 PLUS and Cybernetics schemes. It features digital circuits for significant functions, allowing monitoring and control through Corsair’s iCUE application. This PSU is suitable for a quiet gaming system, with a noise rating of 25-30 dBA and several protections like Over Voltage and Over Temperature Protection.
Together, these components provide a powerful, efficient, and highly customizable platform suitable for demanding computing tasks and high-end gaming setups.

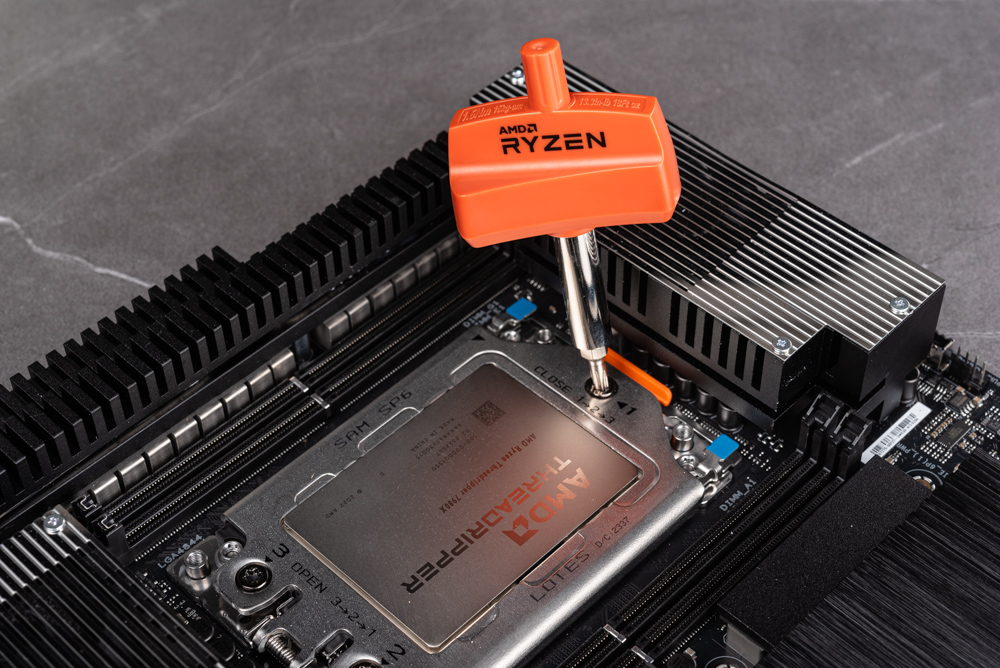
The packaging for the latest Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series processors adopts a more understated design. The exterior of the box features AMD’s distinctive orange stripe logo prominently displayed on the front. On the rear, you’ll find the specific model number of the processor. Inside, the box is thoughtfully designed with protective foam, which securely houses the processor itself. It includes essential accessories such as a water-cooling bracket and a torque wrench, ensuring that you have everything needed for installation right out of the box.
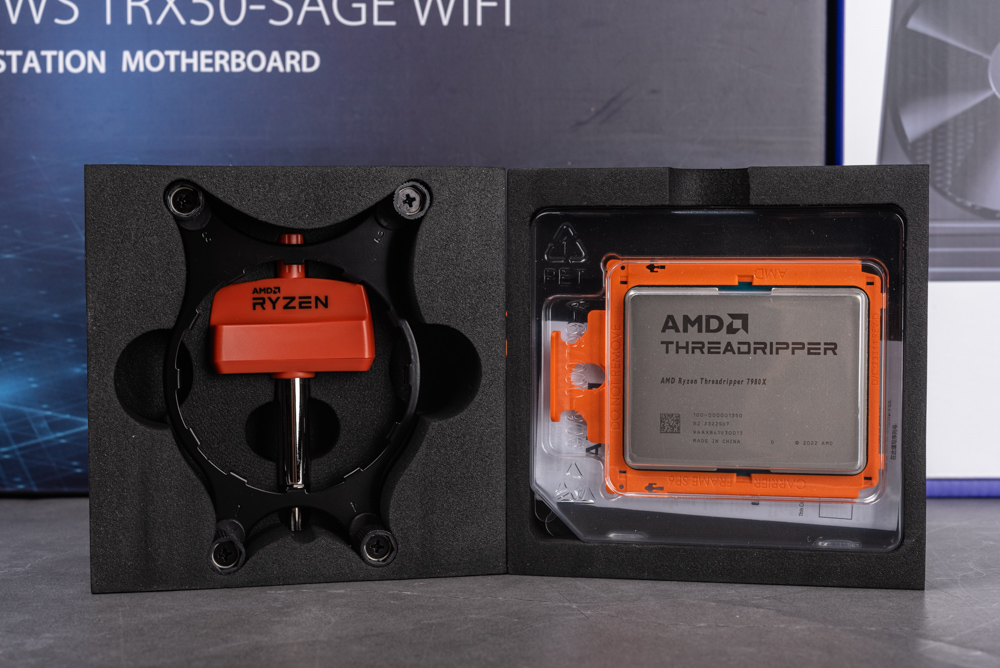
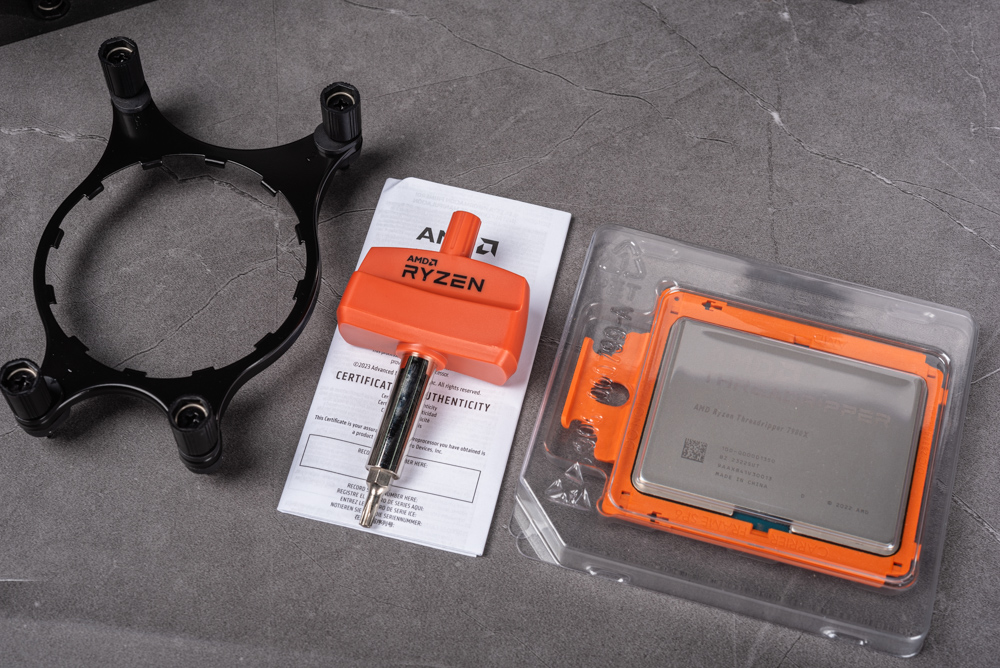



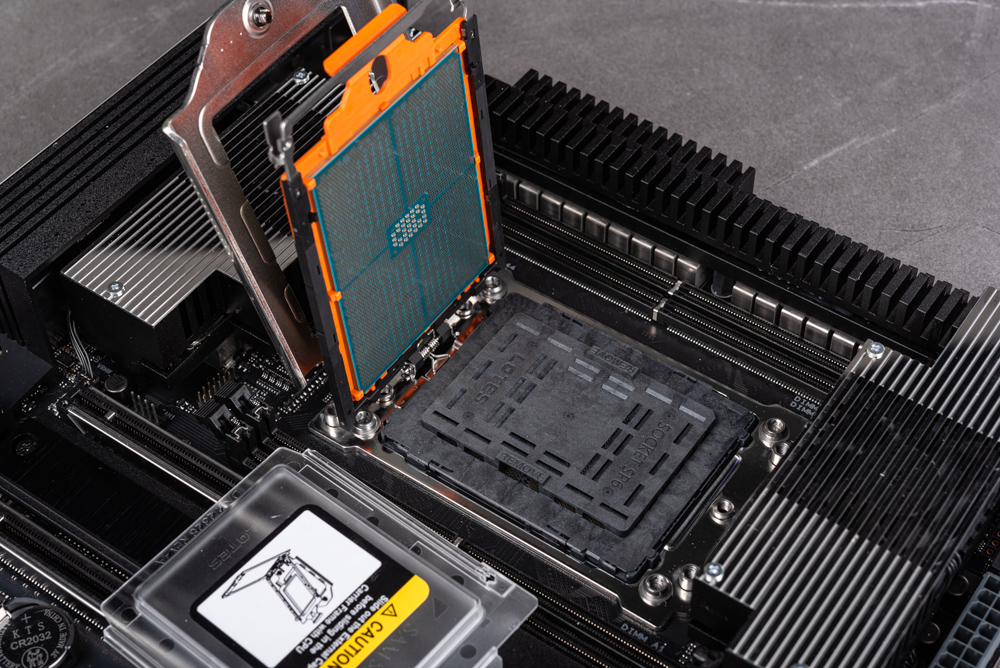
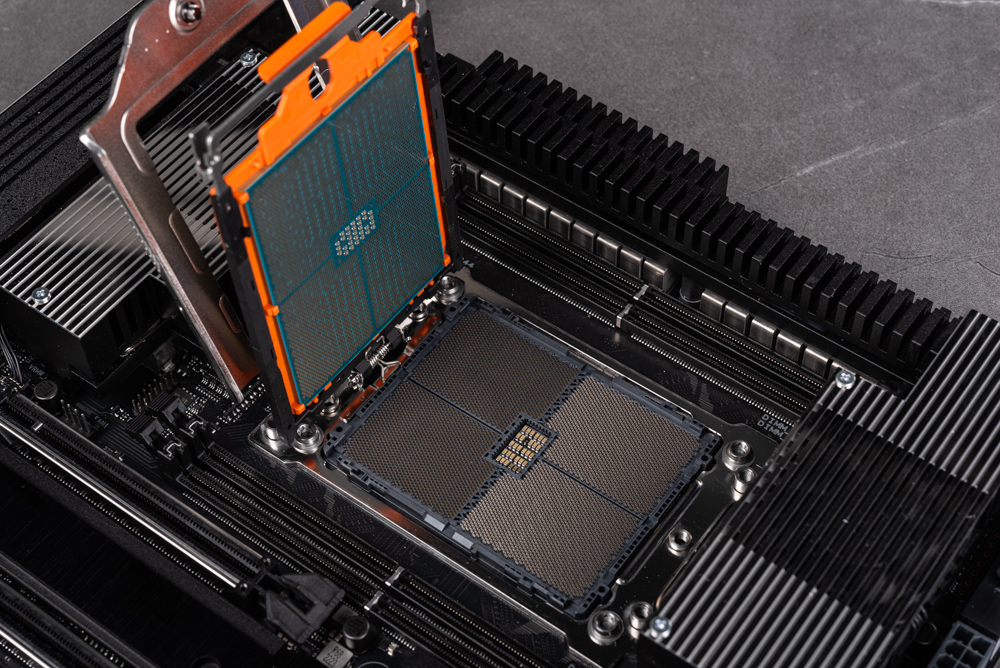
Our evaluation focuses primarily on the Ryzen Threadripper 7980X and 7970X models. This choice is rooted in the understanding that the performance of the 7960X is likely comparable to that of the 7950X. A notable feature of these high-end desktop (HEDT) processors is their increased size. To accommodate this, they are equipped with a specialized carrier frame. This frame is specifically designed to ensure a secure fit of the processor in the sTR5 socket, enhancing stability and performance.

The ASUS Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI motherboard stands out with its robust power supply design, boasting an impressive 36-phase (18*2) +3+4+4 Teamed Power configuration. This design is further enhanced by the inclusion of two strategically placed fans, located beneath the large VRM radiator on both the left and right sides. These fans are pivotal in replacing the VRM power supply, thereby facilitating active cooling. The motherboard is designed to support a dual PSU power supply system, catering to the high-end power requirements of flagship users who engage in PBO and manual overclocking. This makes it an ideal choice for enthusiasts seeking extreme performance and reliability.
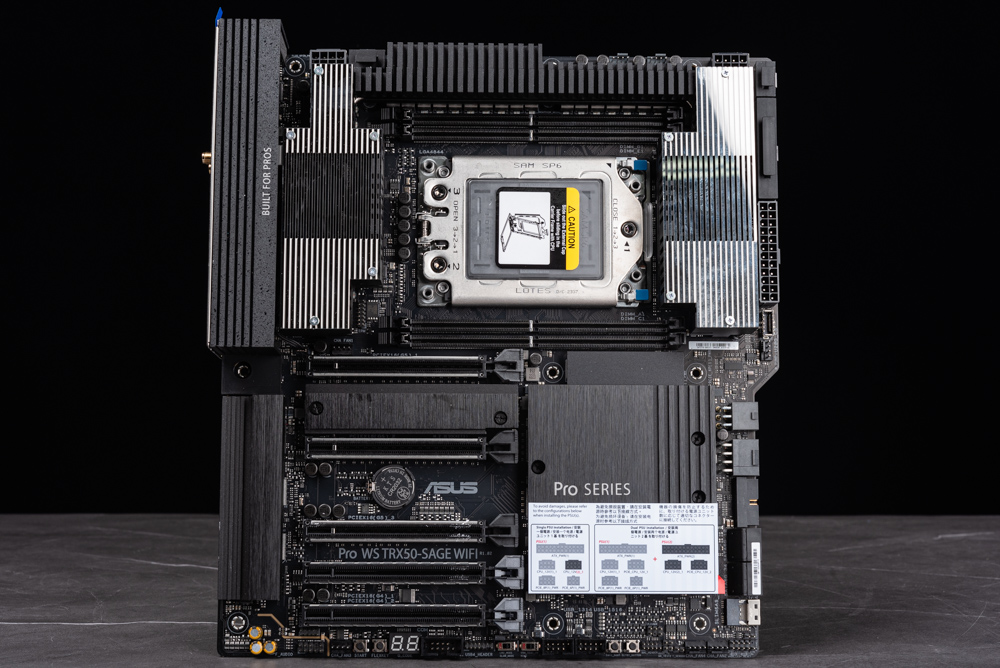

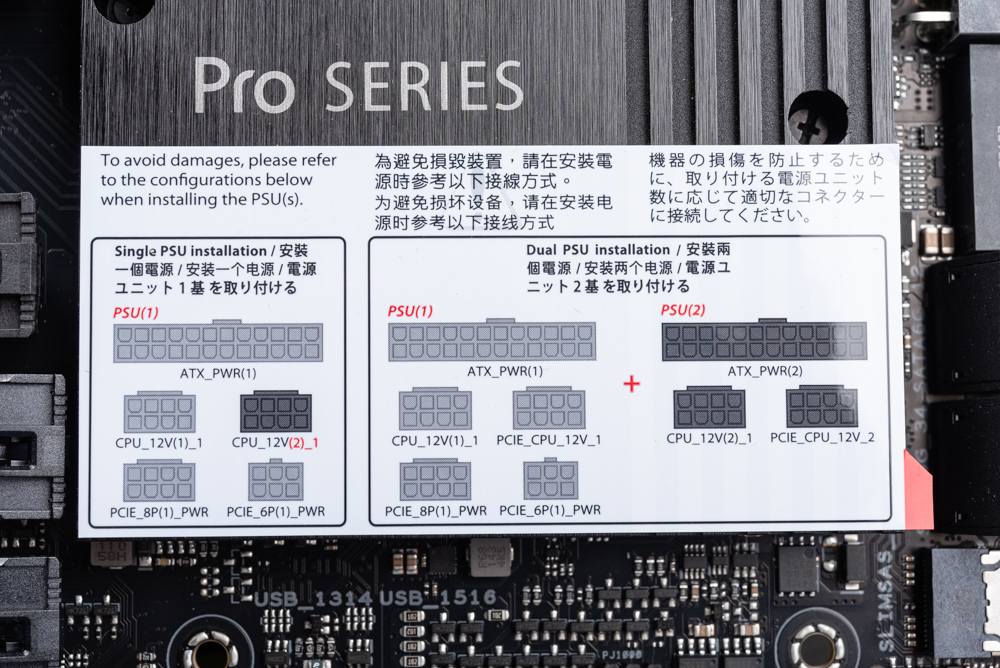

The Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI motherboard maximizes the use of the processor and chipset I/O capabilities to accommodate multiple GPU setups. It features three PCIe slots: the 1st, 2nd, and 3rd slots are PCIe 5.0 compatible, offering x16, x16, and x8 bandwidth respectively. There are two more PCIe slots supporting PCIe 4.0, with x16 and x4 bandwidths respectively.
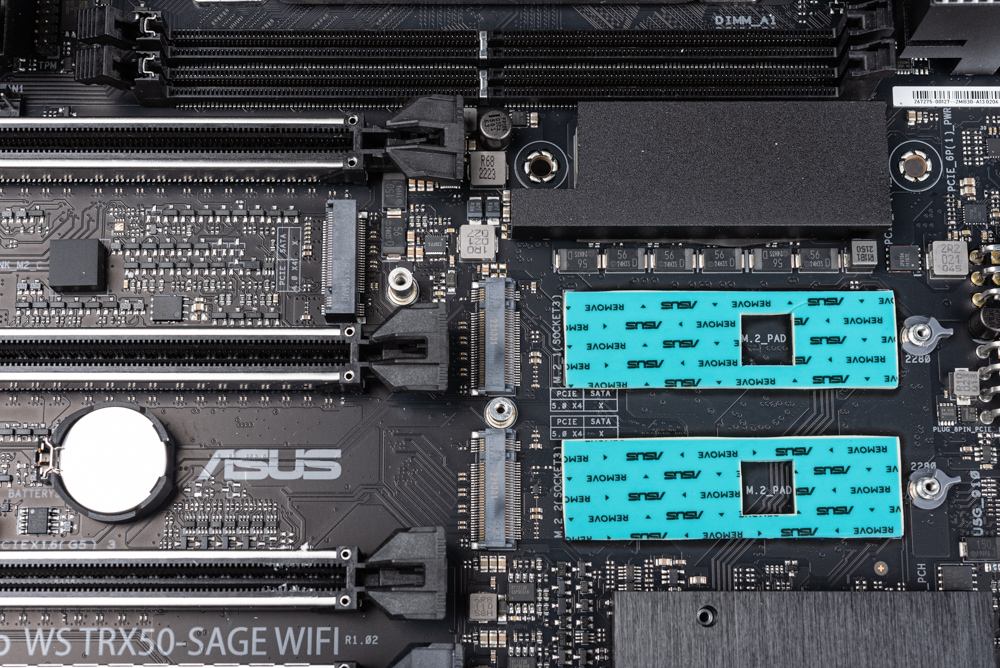
In terms of storage options, this motherboard comes equipped with a combination of 3 M.2 slots and 4 SATA ports. The M.2_1 and M.2_2 slots leverage the PCIe 5.0 x4 channels from the CPU, while the M.2_3 slot supports PCIe 4.0 x4. Another standout feature is a SlimSAS connector located on the lower right edge of the motherboard, which supports PCIe 4.0 x4 NVMe devices, further expanding its storage capabilities.
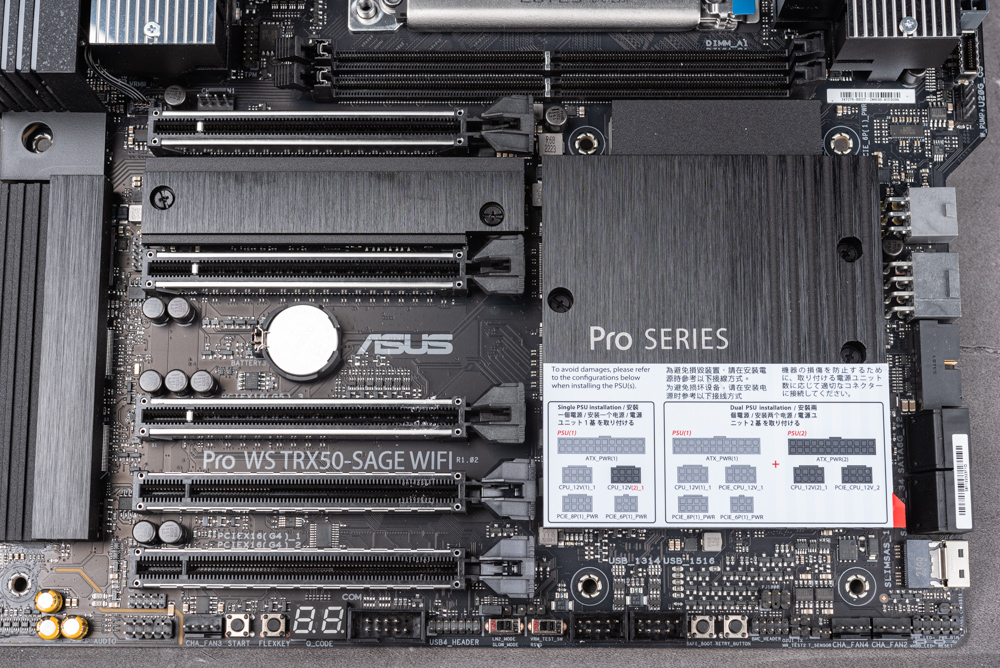
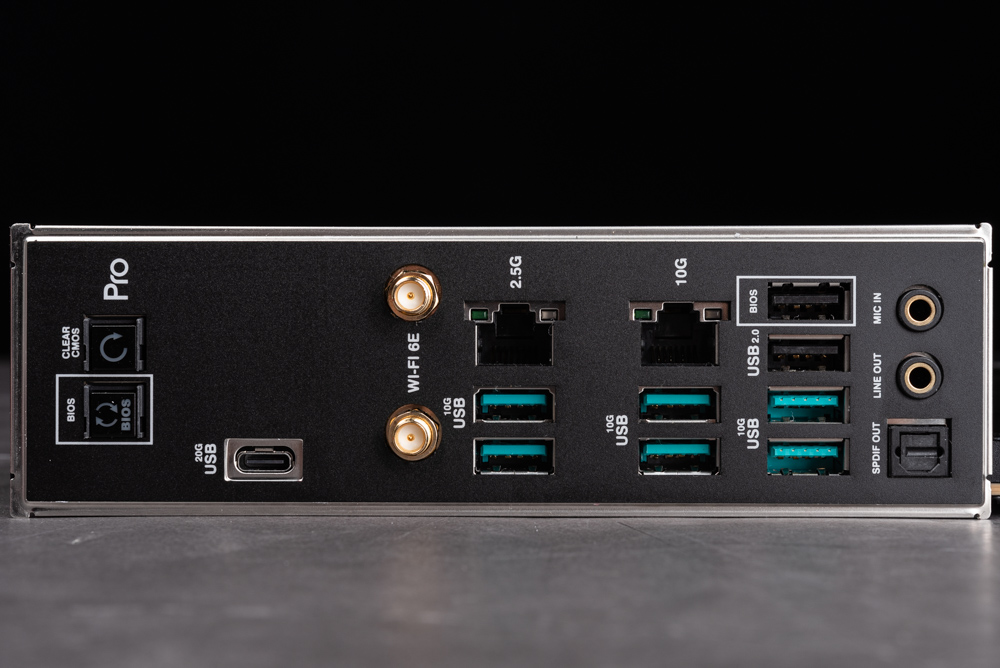
The Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI motherboard’s rear I/O is notably comprehensive, featuring an integrated back panel equipped with Clear CMOS and BIOS Flashback buttons. Connectivity options are extensive, including a USB-C port with 20Gbps speed, six USB ports with 10Gbps, and two USB 2.0 ports. It also boasts dual wired network interfaces: an Intel I226-LM 2.5GbE and a Marvell AQtion 10GbE. For wireless connectivity, it is fitted with Wi-Fi 6E, though there are reports that models sold through retail channels may be upgraded to Wi-Fi 7 specifications.
The motherboard also excels in front USB expansion, offering a USB-C 20Gbps port supporting 27W PD/QC4+ fast charging, two USB 5Gbps ports, and four USB 2.0 expansions. Audio is handled by a basic Realtek ALC1220P chip. It provides nine PWM FAN sockets, a COM port, USB4 expansion, and specialized features like LN2 / Slow Mode among others, catering to a wide range of user needs.

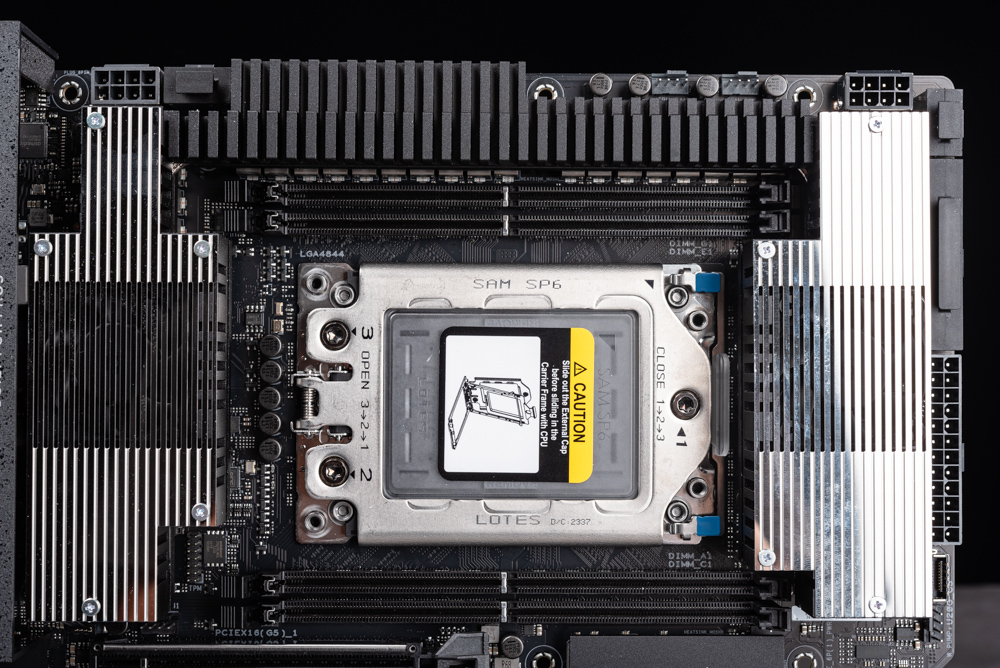
Installing the processor on the motherboard is a precise yet straightforward process. Begin by utilizing a torque wrench to unlock the socket. Next, carefully remove the transparent protective cover located at the center. Gently slide the processor along with its frame onto the designated track. After this, lift the foot protective cover and sequentially remove the processor and buckles. The final step involves pressing down the setup and methodically tightening the screws in a 1-2-3 sequence using the torque wrench. Continue this process until the torque wrench indicates that the preset value is reached, signaling the completion of the installation.


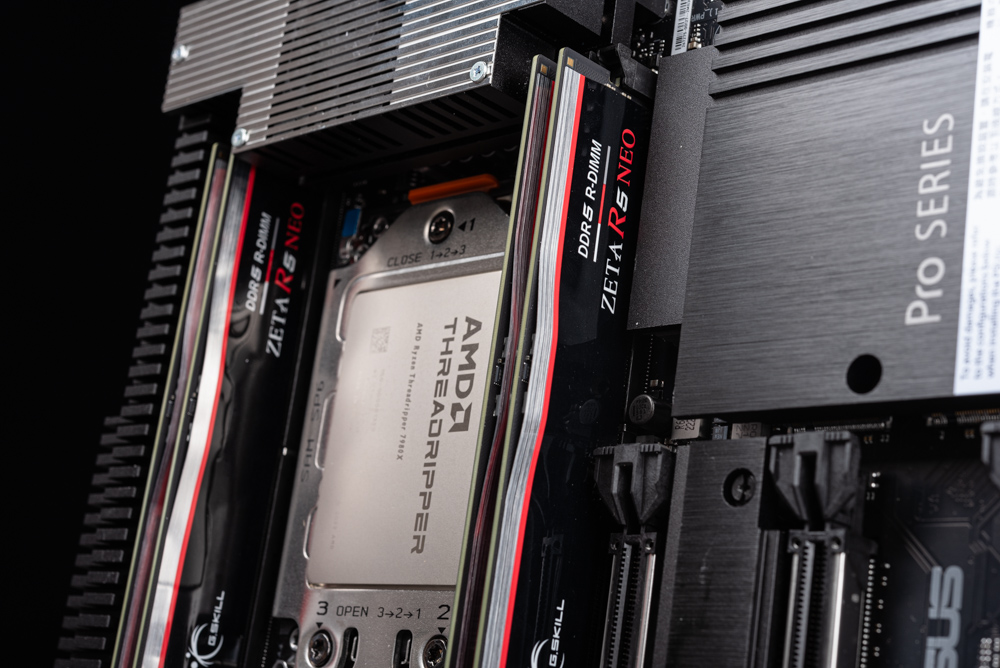
Regarding memory capabilities, this setup employs the G.Skill 128GB 6400MHz EXPO DDR5 RDIMM, consisting of four 32GB modules. The motherboard is designed with a 4-channel 1DPC (one DIMM per channel) configuration, enabling support for up to a massive 1TB of memory capacity. This particular arrangement is especially advantageous for achieving high-clock EXPO overclocking, making it an ideal choice for users who demand high-performance memory solutions.


Test Platform and Settings
This evaluation predominantly centers on the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X and 7970X processors. Due to the unavailability of a comparable Intel Xeon w9-3495X processor, which is not available in retail, comparisons are drawn using data from previous benchmarks. In these tests, the Threadripper 7980X demonstrated superior performance. To provide a broader perspective, mainstream processors like the Ryzen 9 7950X and i9-14900K are also included in the comparison chart, offering insights into the performance variances across different HEDT tasks.
The test setup was meticulously configured with PBO Enhances enabled, DDR5-6400 EXPO memory, an NZXT Kraken 360 water-cooling radiator, and a CORSAIR HX1500i power supply. Below is a detailed breakdown of the test platform for reference:
- Processor: AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X, 7970X
- Motherboard: Pro WS TRX50-SAGE WIFI
- Memory: G.Skill 128GB 6400MHz EXPO DDR5 RDIMM (4x32GB)
- Graphics Card: NVIDIA GeForce RTX 4090
- System Disk: Solidigm P44 Pro 1TB PCIe 4.0 SSD
- Cooler: NZXT Kraken 360
- Power Supply: CORSAIR HX1500i
- Operating System: Windows 11 Pro 22H2
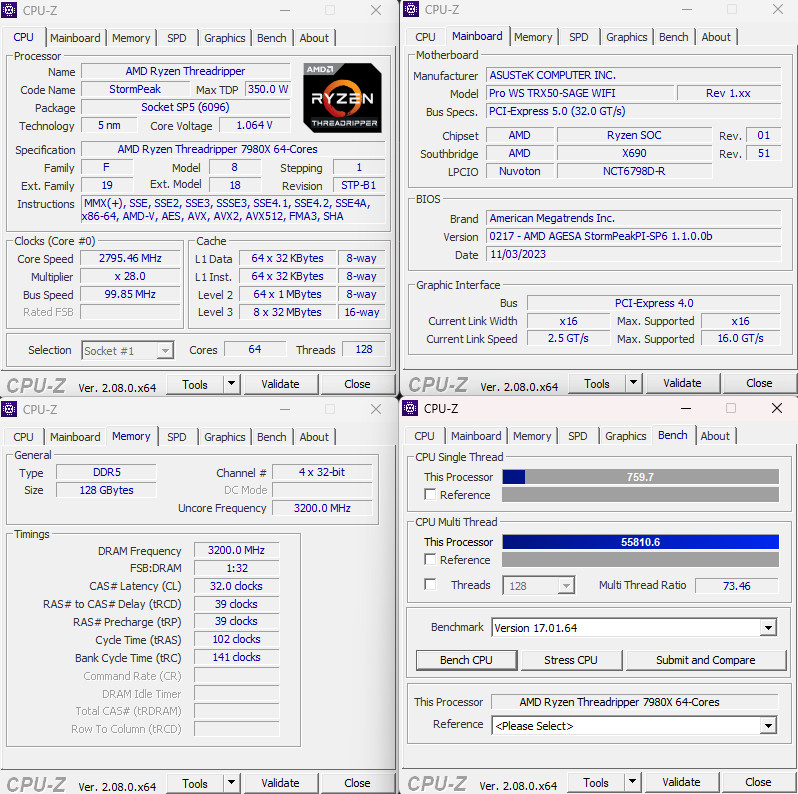
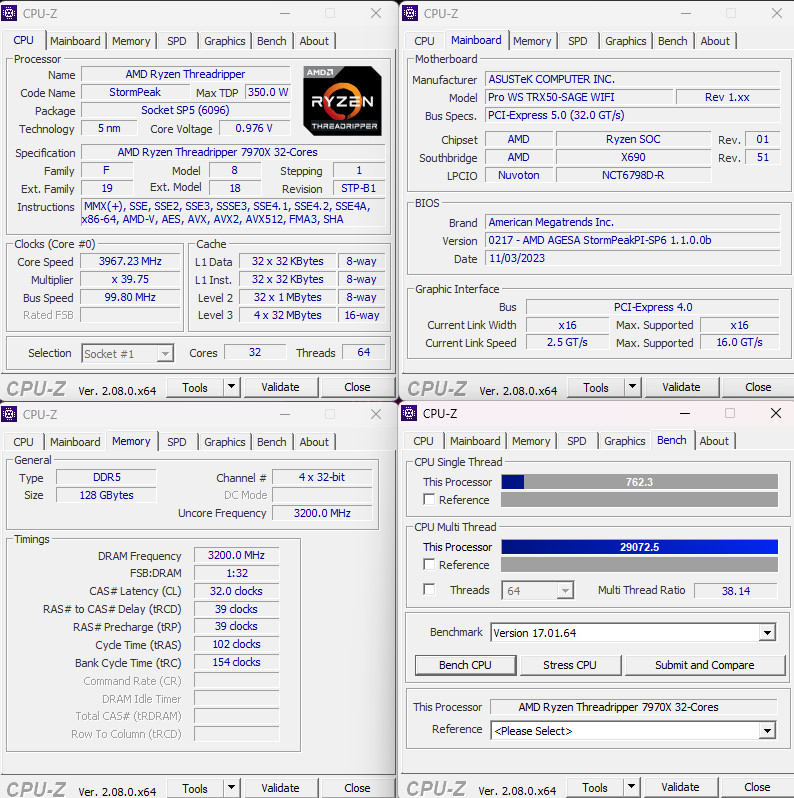
Processor computing performance Cinebench, Corona, VRay, Blender rendering test
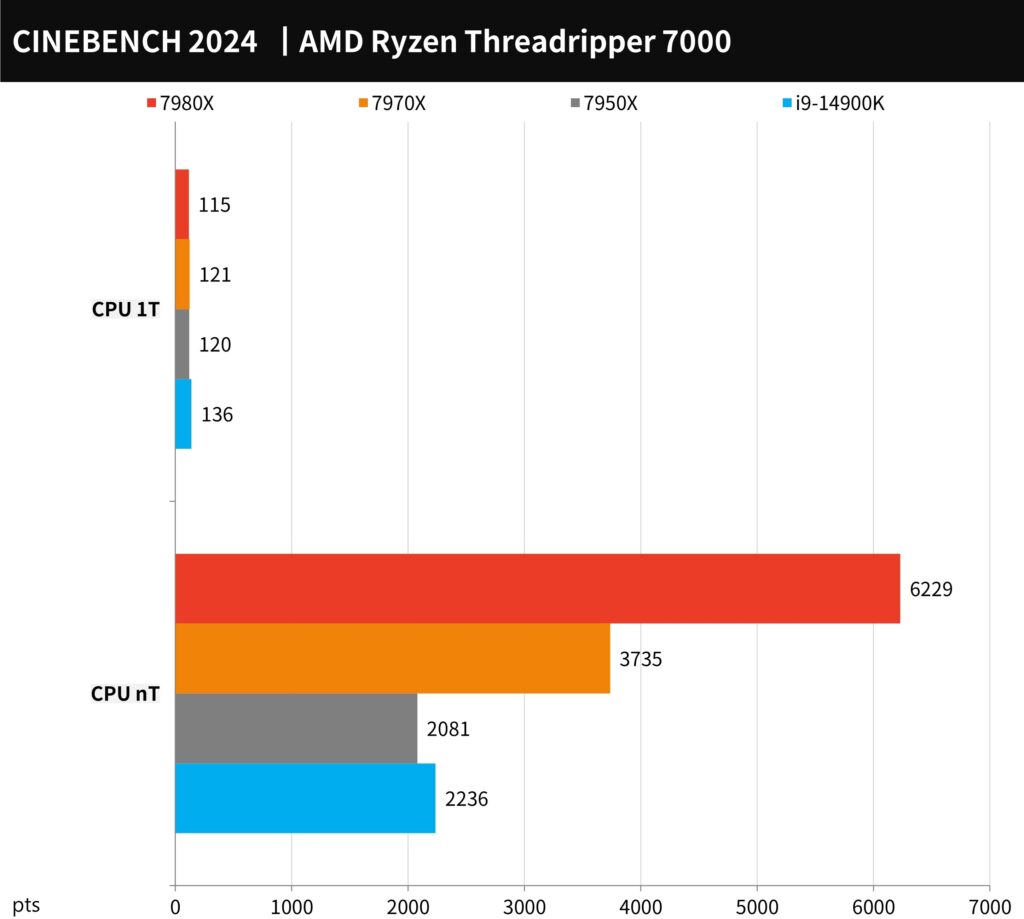
The latest CINEBENCH 2024 version represents a significant upgrade, being entirely developed using the default Redshift rendering engine of Cinema 4D. This version includes comprehensive tests for both GPU and CPU, enabling cross-platform performance comparisons. Notably, this iteration boasts enhanced accuracy and increased speed. The volume of multi-threaded rendering scene calculations has seen a substantial increase — six times that of the R23 version. Consequently, the CPU tests require a minimum of 16GB of memory, while the GPU tests necessitate at least 8GB of VRAM.
In this benchmarking, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved an impressive score of 6229 points in the multi-thread (nT) test, and the 7970X followed with a respectable 3735 points. In the single-thread (1T) test, the 7980X scored slightly lower at 115 points, whereas the 7970X achieved 121 points, aligning closely with the performance of the 7950X.
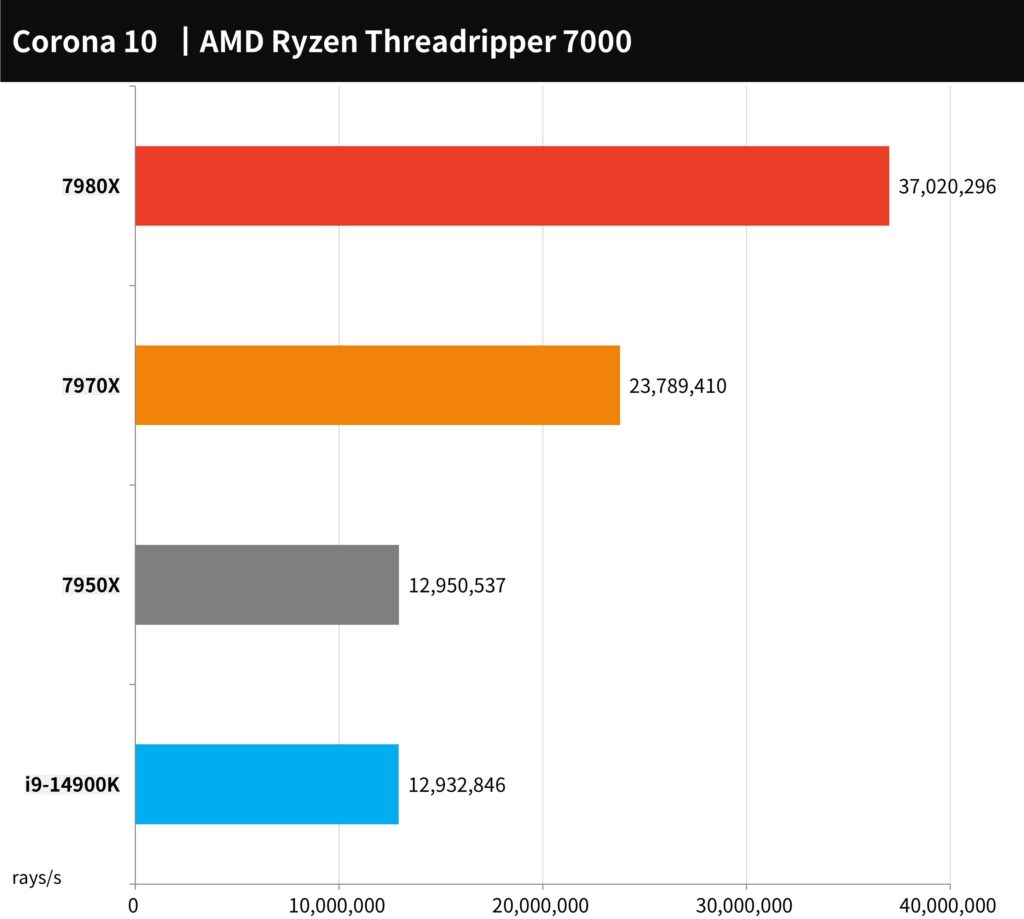
The updated Corona Benchmark, leveraging the Corona 10 rendering core, offers a straightforward yet effective test method. It primarily utilizes a one-minute duration to assess the processor’s capability in terms of rendering rays per second (rays-per-second). In this benchmark, a higher score is indicative of superior performance.
In these tests, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X demonstrated exceptional performance, achieving a rate of 37,020,296 rays per second. Meanwhile, the 7970X also showcased its high multi-core efficiency with an impressive rate of 23,789,410 rays per second.
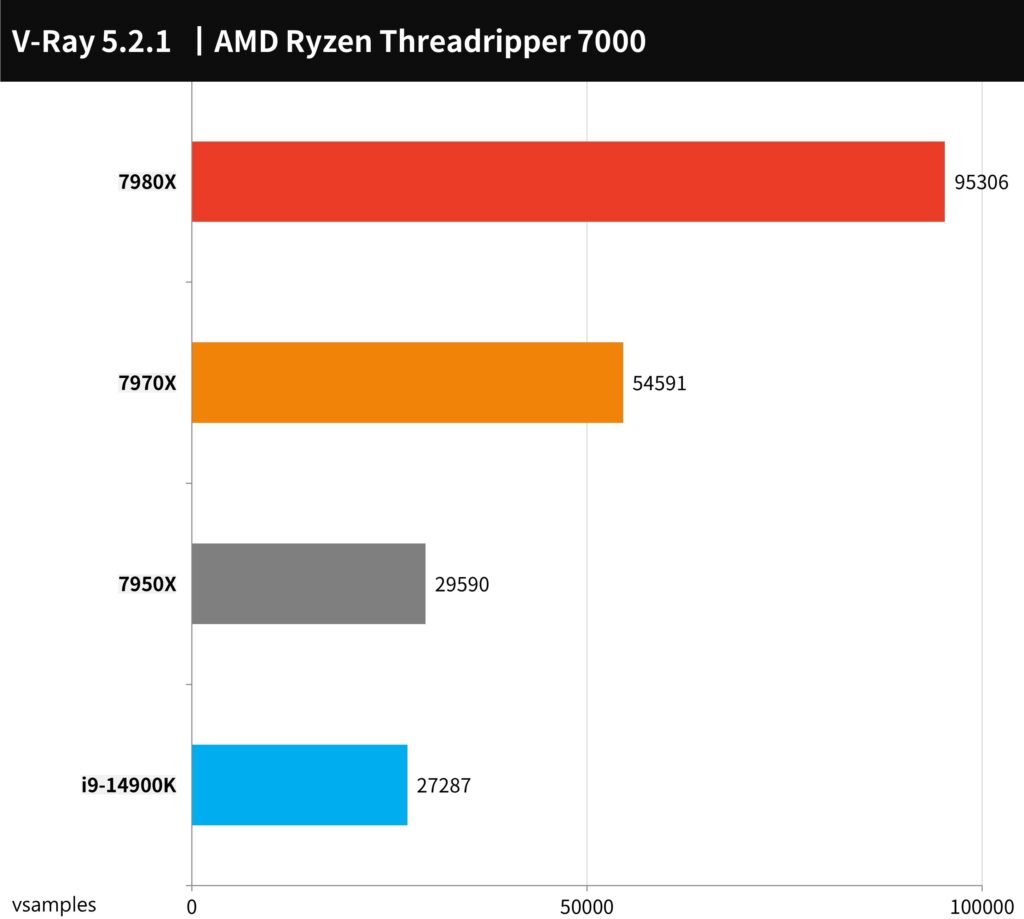
The V-Ray Benchmark, developed by Chaos Group, is a sophisticated tool designed for light rendering based on physical principles. This benchmarking software is adept at evaluating the ray tracing rendering capabilities of CPUs, with the performance measured in ‘vsamples’ per second.
In this rigorous test, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X showcased its formidable power, achieving an impressive 95,306 Samples per second. The 7970X also displayed robust performance, reaching 54,591 Samples per second.
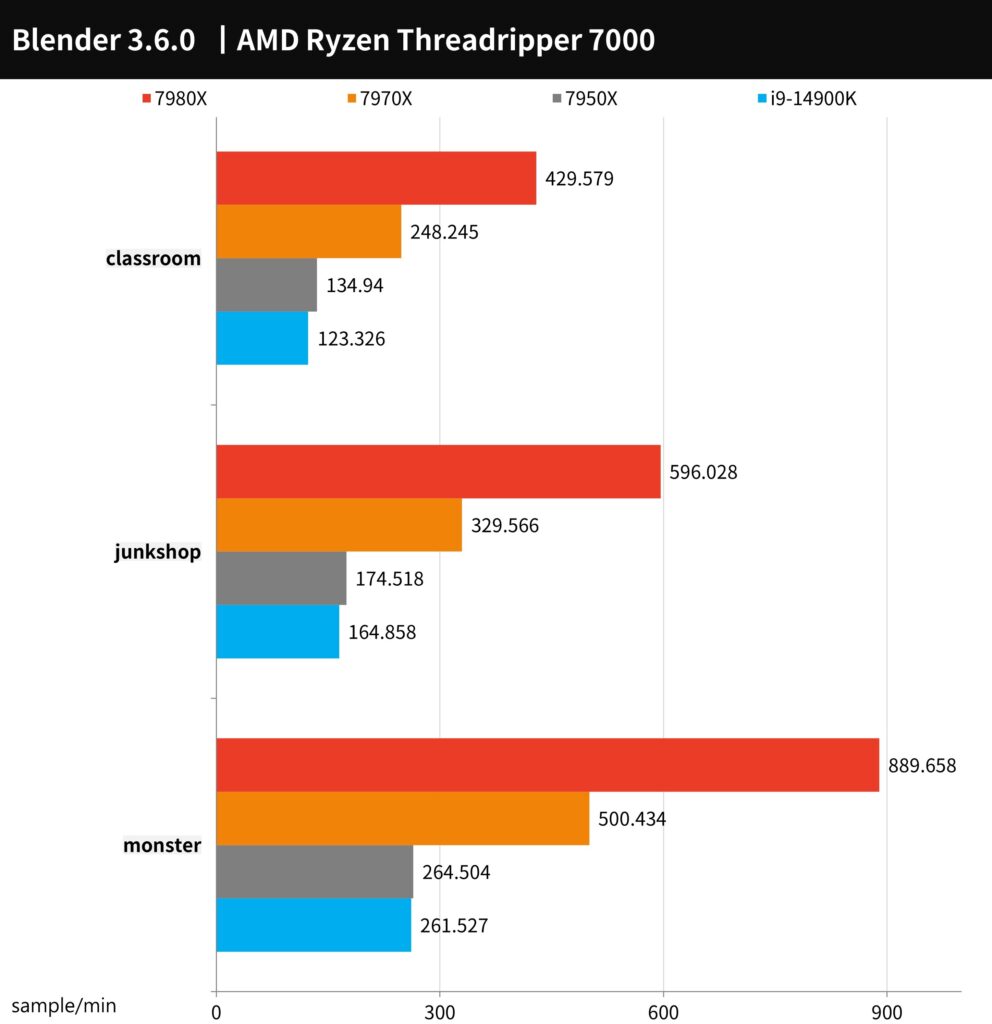
Blender is a versatile, open-source 3D creation tool that is cross-platform compatible. It offers comprehensive support for both CPU and GPU rendering acceleration, and is equipped with a wide array of 3D functionalities including Modeling, Rigging, Animation, Simulation, Rendering, Compositing, and Motion Tracking.
In terms of rendering performance, the results highlight significant differences. The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X takes a clear lead in multi-core performance, showing an improvement of approximately 60-70% over the 7970X. In a similar vein, the 7970X outperforms the mainstream 7950X, which boasts the highest core count in its category, by about 70-80%.
Creation PS, LR image editing, DaVinci Resolve image output test
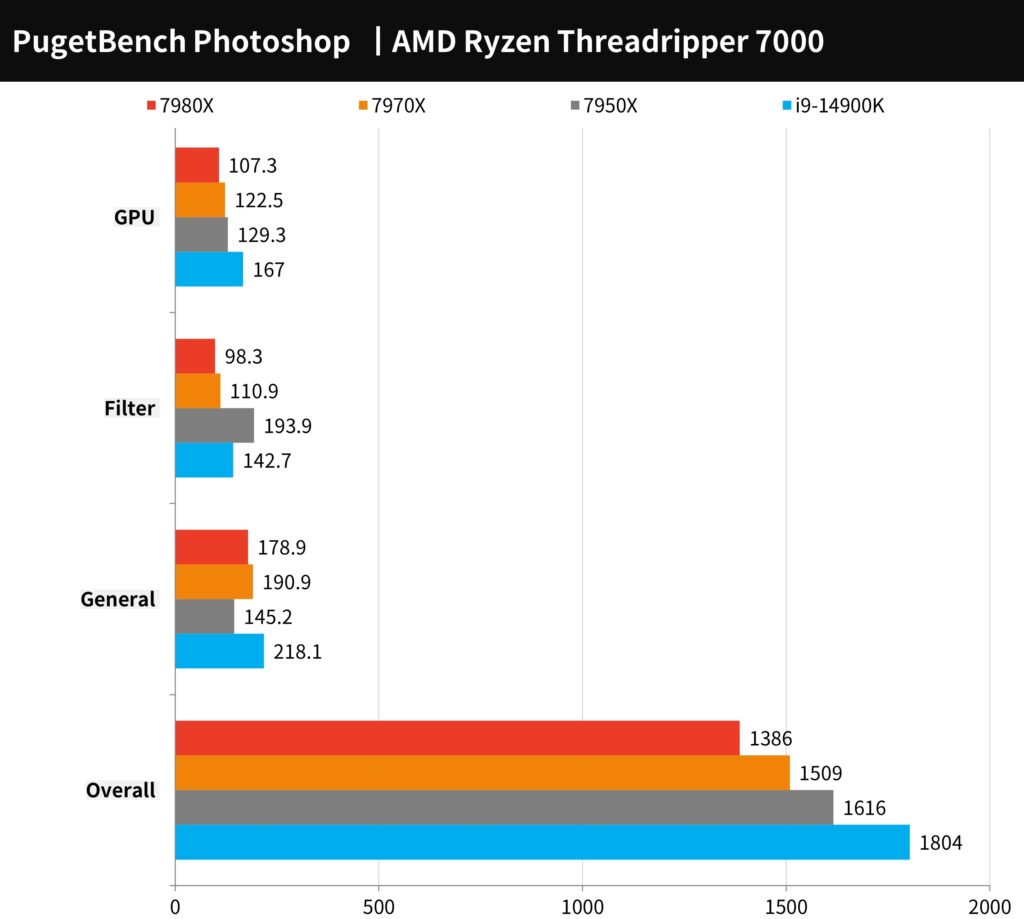
The PugetBench for Photoshop test is specifically designed to assess performance using Photoshop’s most common functions, divided into ‘General’ and ‘Filter’ tasks. The ‘General’ tasks involve processing 18MP.CR2 RAW images through a series of operations including reduction to 500MB, rotation, magic wand selection, Mask Refinement, Paint Bucket, Gradient, Content Aware Fill, and saving and opening. PSD files. The ‘Filter’ tasks focus on applying various operations like the Camera Raw Filter, lens correction, noise reduction, automatic sharpening, tilt-shift blur, aperture blur, adaptive wide-angle, and liquefaction. These tests are conducted three times, with scores calculated on a 1000-point scale, where higher scores indicate better performance.
In this benchmark, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved a total score of 1386 points, while the 7970X scored 1509 points. The results suggest that Photoshop’s processing doesn’t necessarily benefit from a high-core platform, as evidenced by the lower performance compared to the 7950X.
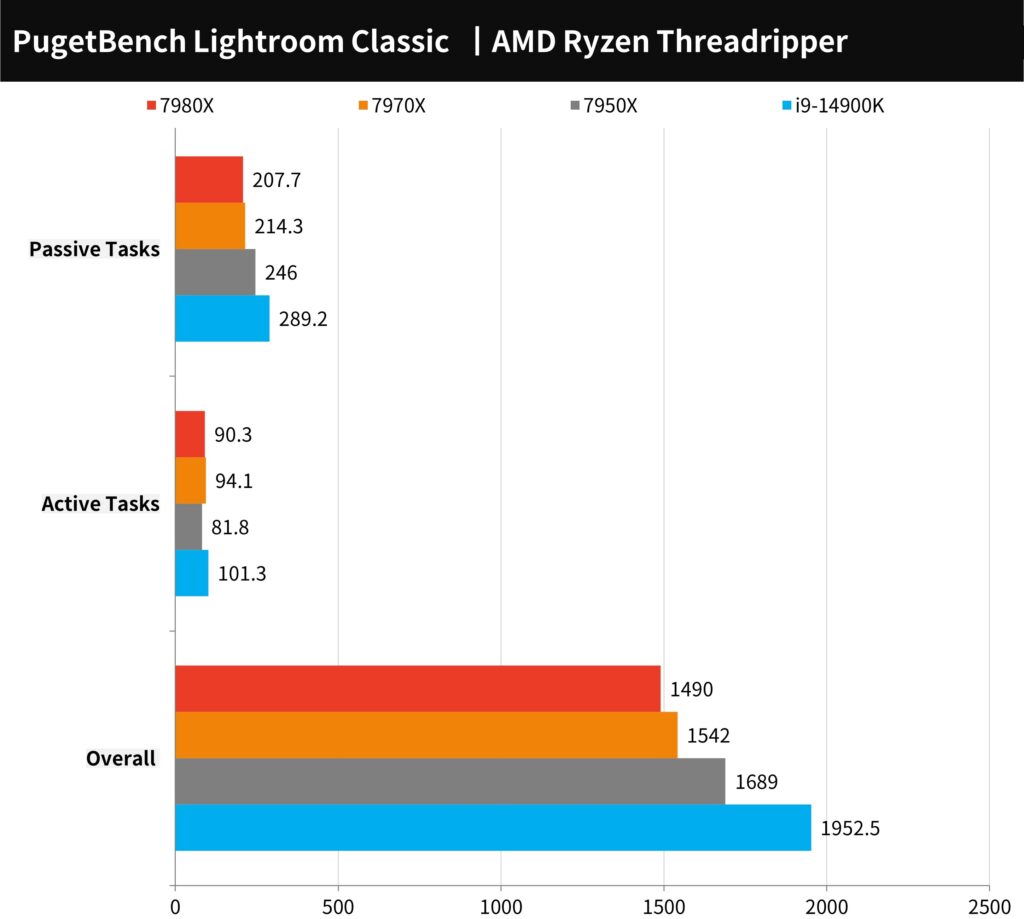
The PugetBench for Lightroom Classic benchmark involves creating a library of 500 photos, encompassing images from Canon EOS 5D Mark III – 22MP.CR2, Sony a7r III – 42MP .ARW, and Nikon D850 – 45MP.NEF. This test is divided into active and passive tasks. Active tasks test the efficiency of enlarging, viewing, switching, and auto WB/Tone operations in the Lightroom photo library. The passive tasks include importing 500 photos, creating smart previews, merging panoramas and HDRs, and exporting various formats like JPEG and DNG. The scoring is out of 1000 points, with higher scores denoting better performance.
In this benchmark, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved a total score of 1490 points, while the 7970X scored 1542 points. Similar to the results in Photoshop testing, Lightroom Classic also appears to deliver better performance on general mainstream platforms.
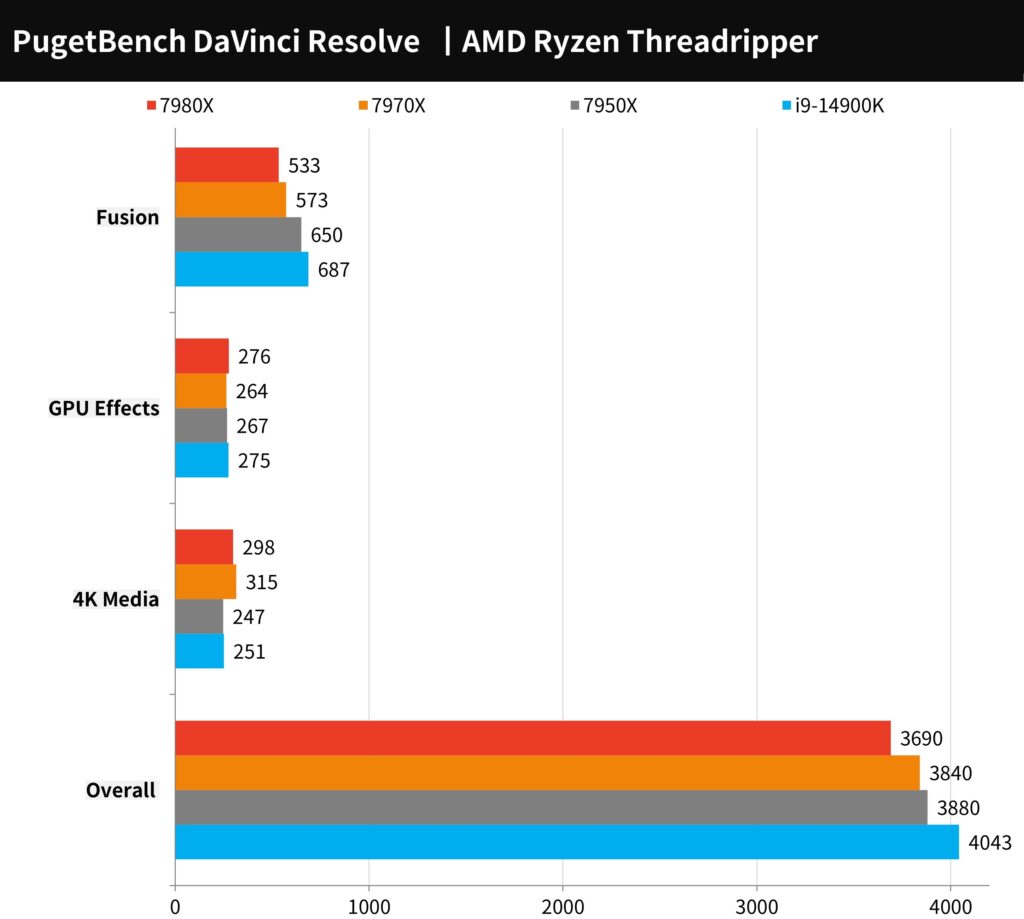
The PugetBench for DaVinci Resolve test is specifically designed to evaluate video creation performance on computers, focusing on both 4K and 8K image processing. This benchmark includes a variety of media formats like 4K H.264 150mbps 8-bit, 4K ProRes 422, 4K RED, 8K H.265 100mbps, and 8K RED. It also incorporates testing with OpenFX and GPU-accelerated Fusion special effects to assess the machine’s capabilities in handling demanding video tasks.
In this rigorous evaluation, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved a total score of 3690 points, while the 7970X scored 3840 points. These results suggest that mainstream platforms may offer superior performance for this type of workload. However, it’s worth noting that this could be attributed to the memory requirements for the project not being extensive enough to fully utilize the capabilities of the HEDT (High-End Desktop) platform.
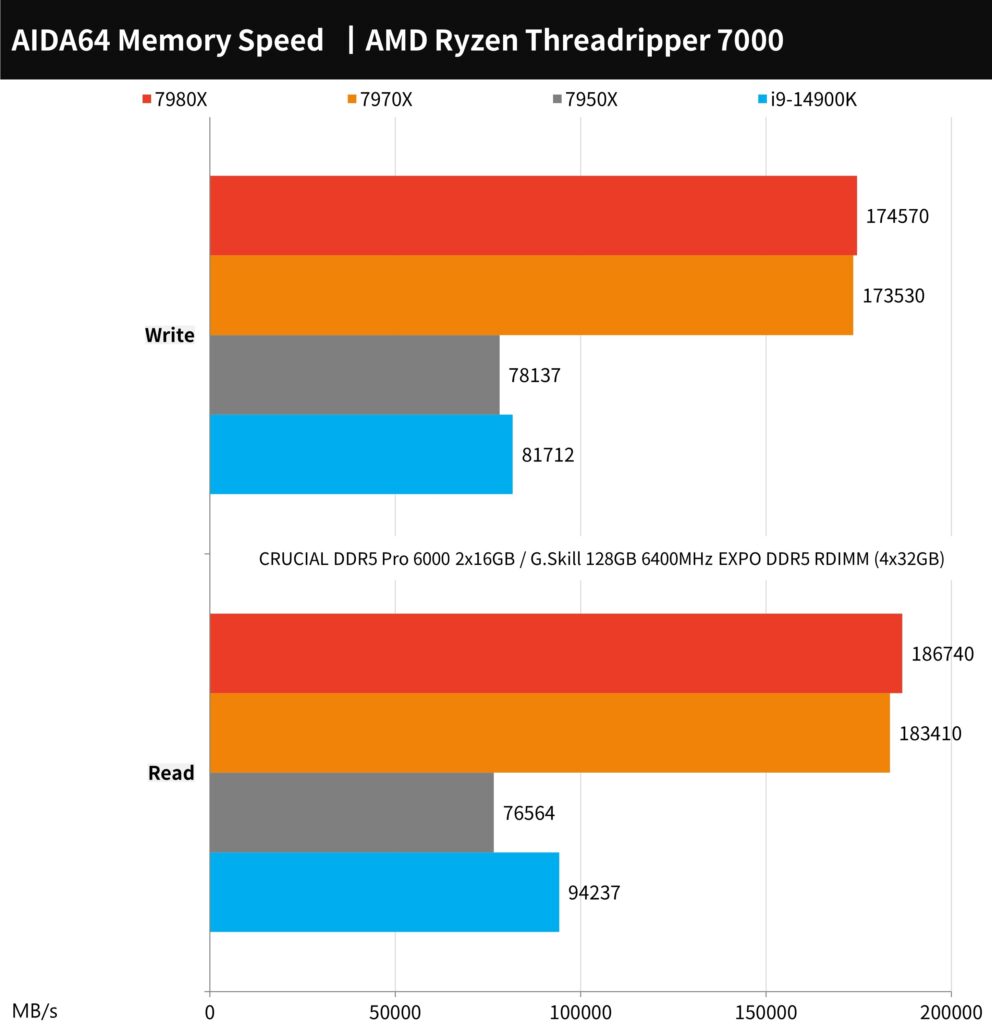
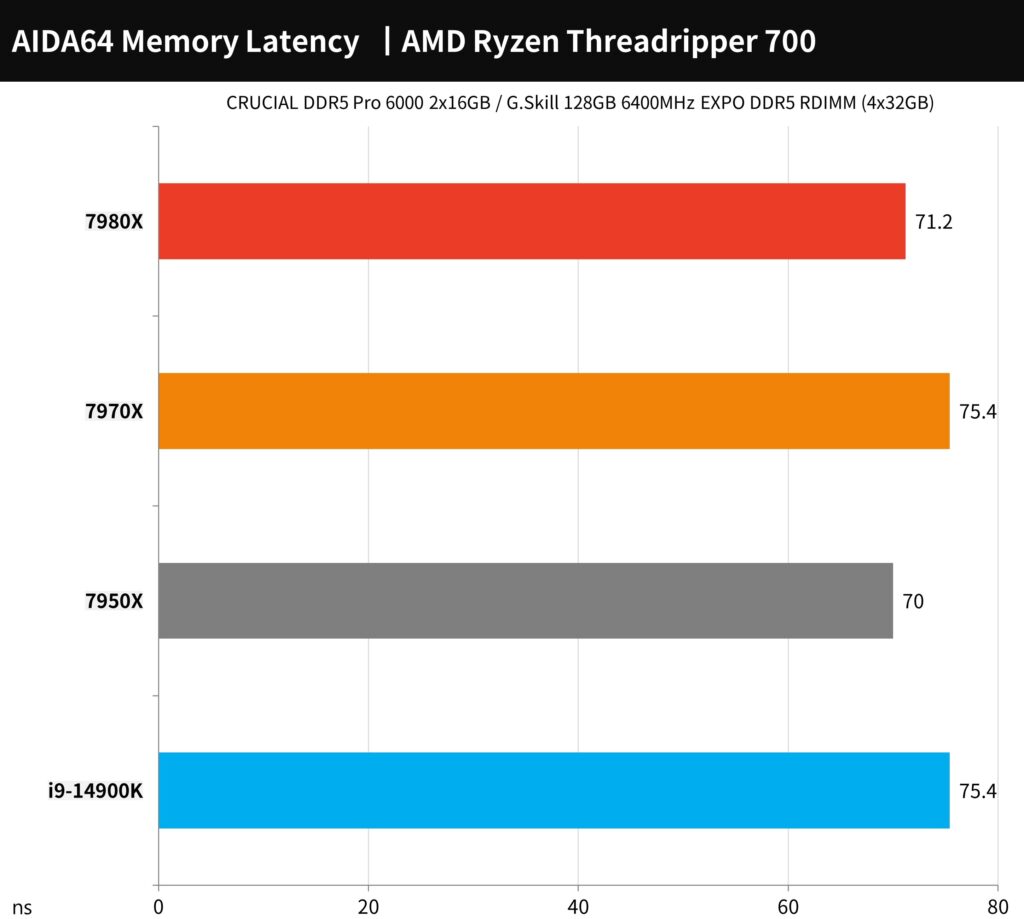
AIDA64 memory, WinRAR / 7-Zip performance test
In the AIDA64 memory test, the setup included the G.Skill 128GB 6400MHz EXPO DDR5 RDIMM memory, composed of four 32GB modules. Both the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X and 7970X processors utilize a quad-channel memory architecture. When paired with this high-speed 6400MT/s memory, they achieve exceptionally high memory read and write bandwidths. Specifically, the transmission bandwidths reach up to 186,740 MB/s for reading and 174,570 MB/s for writing. The memory latency is recorded at 71.2ns for the 7980X and 75.4ns for the 7970X.
WinRAR, widely recognized as a leading compression tool, showcases distinct performance levels with these processors. In our tests, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved a compression speed of 68,016 KB/s. Interestingly, the 7970X outperformed this with a higher compression speed of 77,866 KB/s. This superior performance of the 7970X in WinRAR can be attributed to its higher clock speed, demonstrating its efficiency in compression tasks.
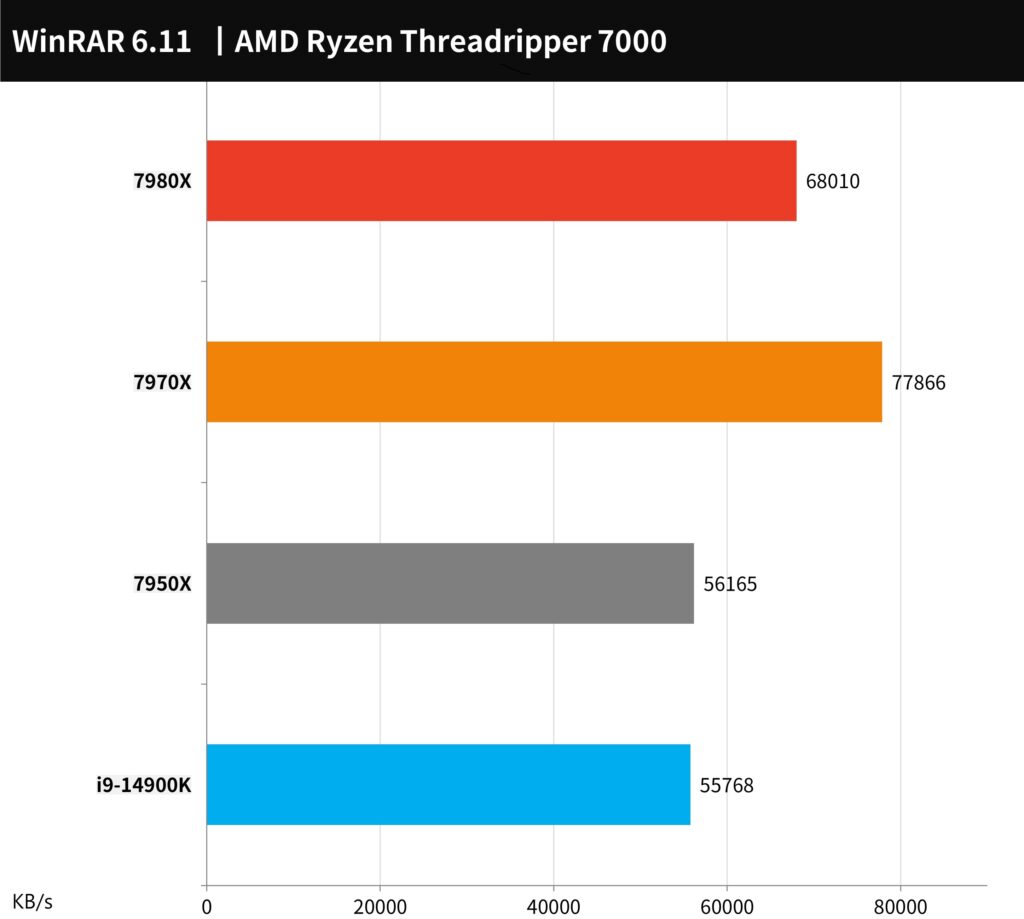
7-Zip, another renowned and free compression tool known for its effective use of multi-core performance, shows impressive results with these processors. The AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved an ultra-high performance, registering 481.676 / 386.107 GIPS. Close behind, the 7970X also demonstrated strong performance, with scores of 480.688 / 351.517 GIPS. These results underscore the capabilities of both processors in efficiently handling multi-core compression tasks.
PCMark 10 computer performance test
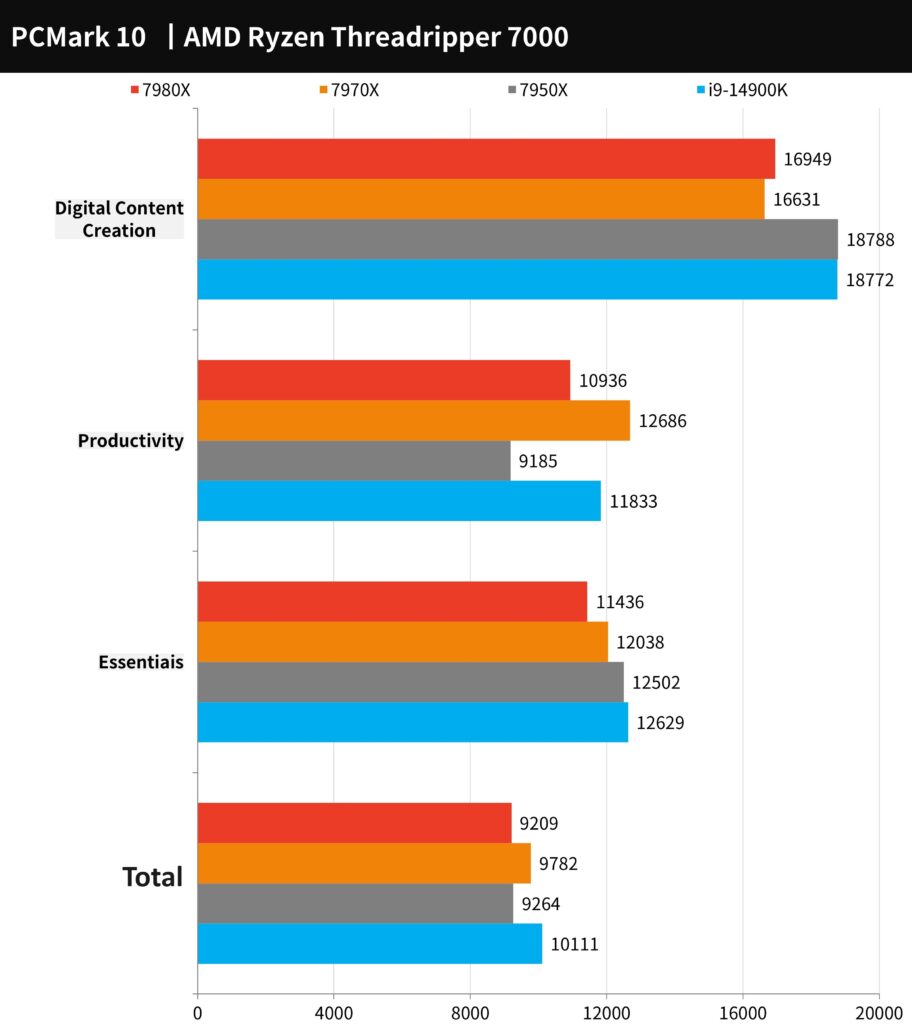
PCMark 10 is utilized to gauge the overall performance of the computer, offering a comprehensive scoring system. It evaluates ‘Essentials’ – basic computer tasks like app startup speed, video conferencing, and web browsing. The ‘Productivity’ test focuses on spreadsheet and word processing capabilities, while ‘Digital Content Creation’ assesses image content creation through tasks like photo/video editing, rendering, and visualization.
In this benchmark, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved a total score of 9209 points, while the 7970X scored even higher at 9782 points. When compared to mainstream platform computer performance, the 7970X shows an edge over the 7950X. This indicates that the latest generation of Ryzen Threadripper processors maintains robust general productivity and computer performance, even with increased clock speeds and core counts.
3DMark CPU performance and Fire Strike, Time Spy benchmark test
The 3DMark benchmark, a widely recognized tool for testing computer graphics and gaming performance, includes tests for both Direct X11 and Direct X12. The Fire Strike test, which is based on Direct X11, yielded scores of 29,667 points for the 7980X and 30,290 points for the 7970X. These results indicate a relatively modest performance in older DX11 games. In the Time Spy test, focused on Direct X12, the 7980X achieved 12,809 points, while the 7970X scored slightly higher at 13,448 points. These findings suggest that for gaming applications, having a higher core count does not necessarily translate to significantly improved performance.
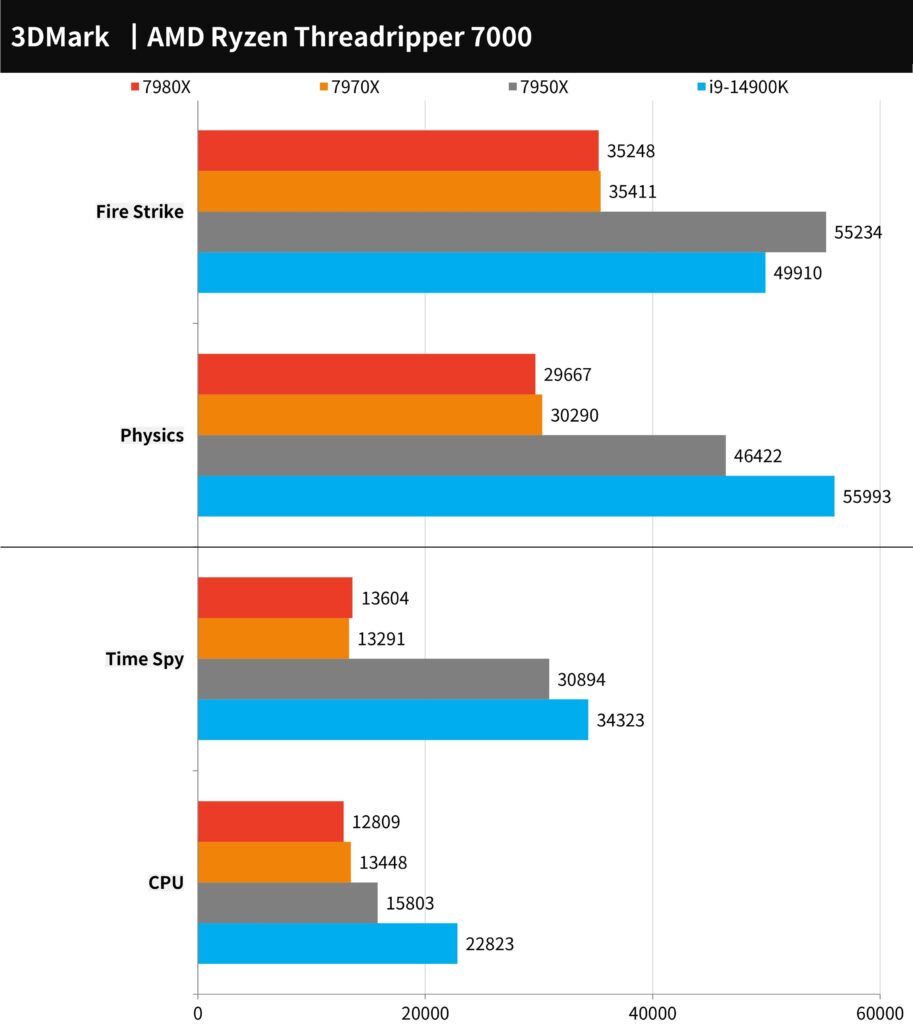
“The 3DMark CPU test specifically evaluates the processor’s capabilities in physical operations and custom simulations. This test methodically assesses performance across different thread counts: 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, and up to the processor’s maximum thread capacity. It’s noteworthy that performance beyond 16 threads is predominantly utilized in 3D rendering, as well as audio and video outputs. Generally, Direct X12 games tend to favor execution on 8 threads, while older games often prefer fewer threads.
In this benchmark, both the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X and 7970X demonstrate robust multi-core performance at maximum threads. However, in scenarios typical of 8T and 4T games, their performance is relatively average, indicating that their strengths in multi-threaded tasks do not necessarily extend to all gaming scenarios.
9+2 AAA e-sports games tested the processor performance.
In our comprehensive gaming performance evaluation, we included nine AAA titles, each representing a range of genres and graphical demands. This diverse set included the entry-level racing game ‘F1® 22’, the adventure-laden ‘Tomb Raider: Shadow of the Tomb Raider’, ‘Horizon: Dawn of Hope’, and the graphically intense ‘Edge 3’. We also tested ‘Red Dead Redemption 2’, ‘Assassin’s Creed: Viking Age’, as well as ‘Trench 6’, ‘Marvel’s Star Trek’, and the ray tracing-supported ‘Electronic 2077’.
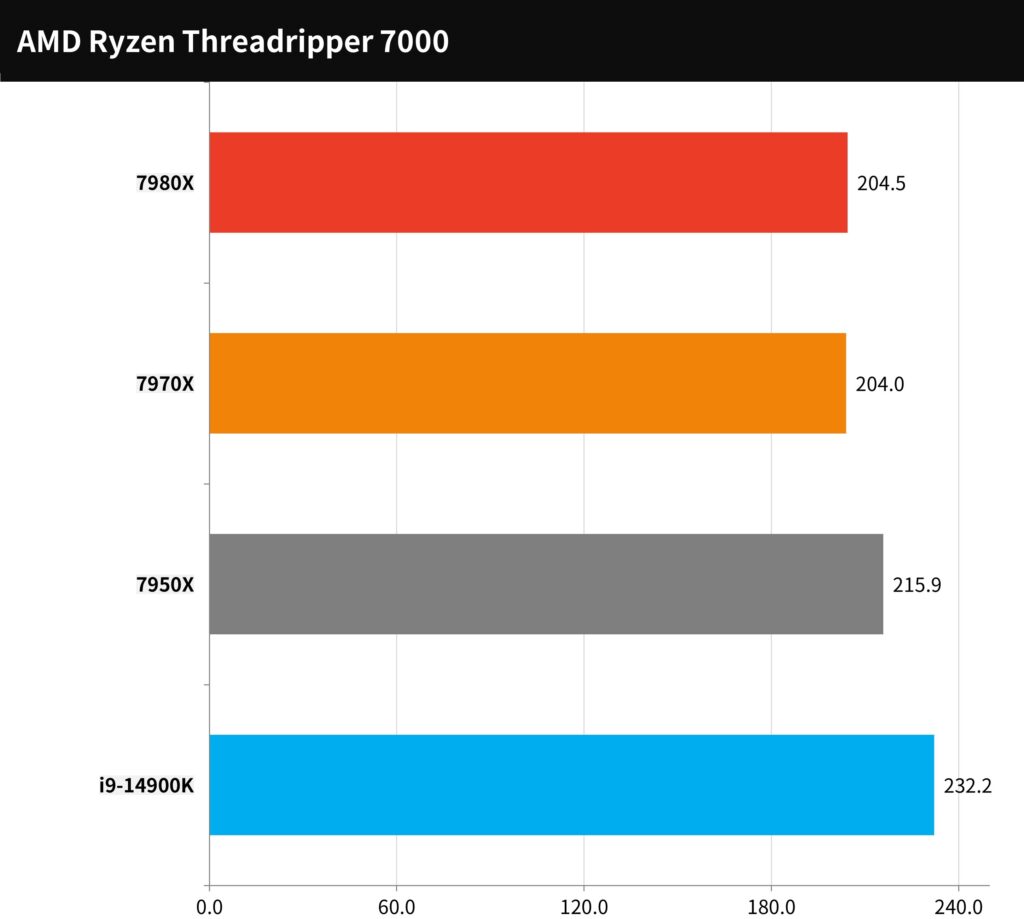
All games were benchmarked using their respective in-game benchmark tools at a resolution of 1080p and the highest default settings provided by the games.
In this array of tests, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X achieved an average framerate of 204.5 FPS, closely followed by the 7970X at an average of 204 FPS. Although these results are slightly lower than the performance of the 7950X, they still fall within an acceptable range for high-level gaming.
E-sports games, known for emphasizing tactical skills and team competition, generally don’t demand high image quality, allowing them to achieve very high average FPS (frames per second) on high-end CPUs and GPUs, particularly at 1080p resolution. At higher resolutions, enhancements in CPU performance and clock speed can further elevate FPS in these games.
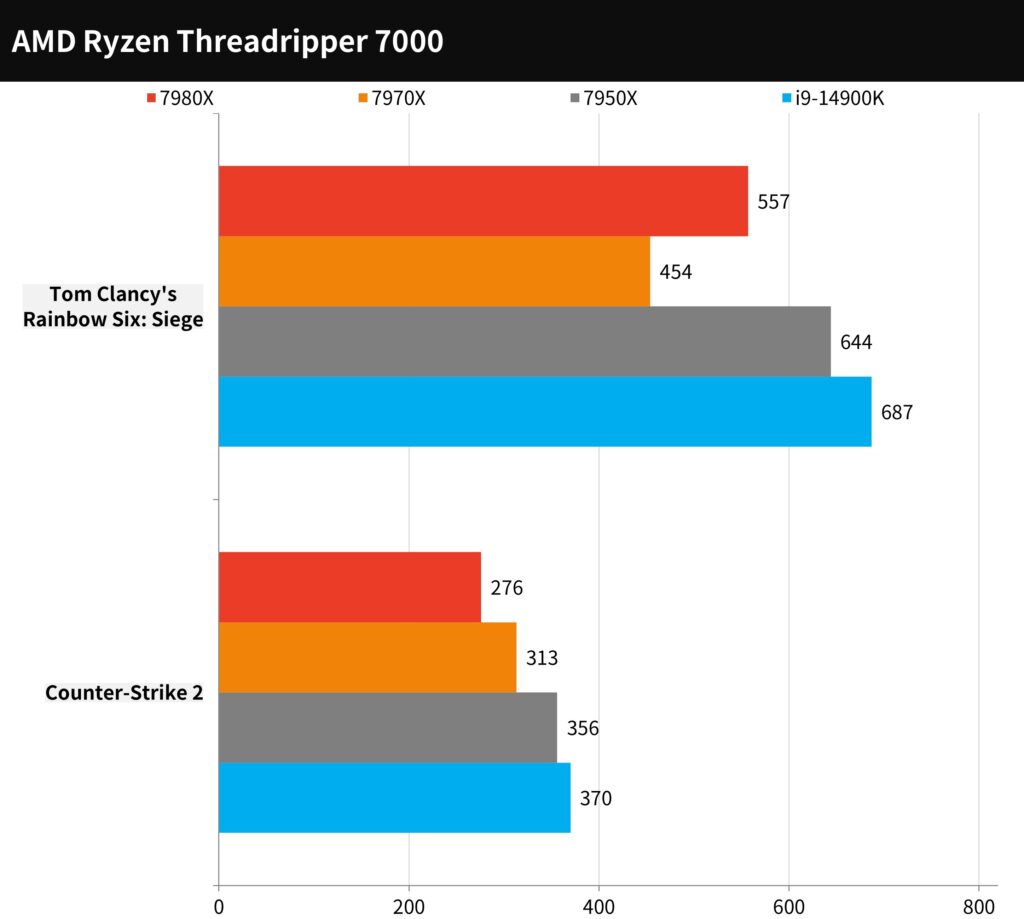
In our tests, we focused on two popular e-sports titles: ‘Counter-Strike 2’ (CS2) and ‘Tom Clancy’s Rainbow Six: Siege’ (R6), conducting benchmarks at 1080p resolution with the games’ highest settings.
The results showed that the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X averaged 276 FPS in CS2 and 557 FPS in R6. In comparison, the 7970X averaged 313 FPS in CS2 and 454 FPS in R6. These outcomes indicate the impressive capability of these processors in handling the fast-paced demands of e-sports gaming.
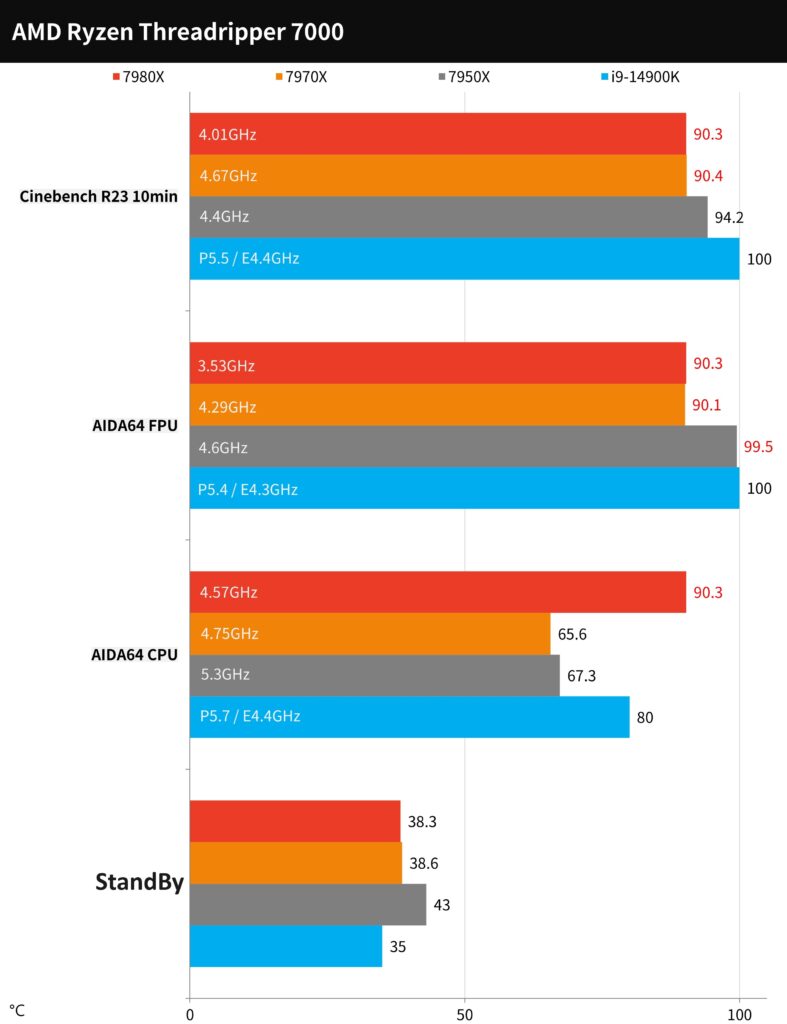
AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X, 7970X processor temperature and power consumption test
In our stress testing regimen, we utilized a 360mm AIO cooling solution, operating the fan and water pump at full speed, to assess the performance under AIDA64 CPU, FPU, and Cinebench R23 burn-in tests. For typical computer usage, the temperature performance in the AIDA64 CPU test is more representative, whereas the FPU test simulates the highest load scenario with increased power consumption.
In the AIDA64 CPU stress test, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X, running at a full-core speed of 4.57GHz, reached a peak temperature of 90.3°C, hitting the upper-temperature limit. The 7970X, operating at 4.75GHz, recorded a significantly lower temperature of 65.6°C. However, during the FPU test, both the 7980X and 7970X reached the upper-temperature limits, a pattern also observed in the Cinebench R23 stress test, indicating that these processors operate at the edge of their thermal capacity under maximum load conditions.
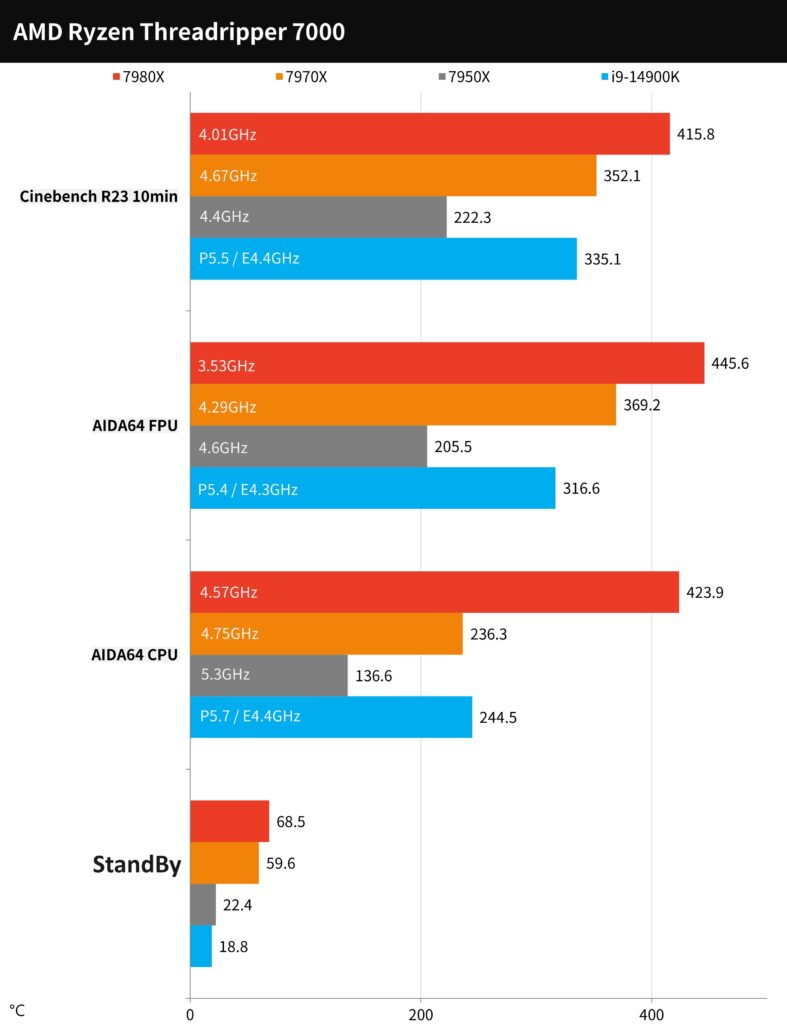
In terms of CPU power consumption, our focus is primarily on the CPU Package Power. During extended stress testing, the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7980X consumes approximately 445W with thermal management measures in place, while the 7970X draws 369W. However, it’s important to note that these figures represent average power consumption during prolonged stress tests. As the processors reach their upper-temperature limits and clock frequencies are reduced, power usage stabilizes.
In contrast, if we look at a single execution of the Cinebench R23 test, the 7980X exhibits an instantaneous power consumption spike of up to 700W, with the entire computer platform exceeding 900W. Meanwhile, the 7970X reaches an instantaneous maximum of around 400W, with the computer platform drawing approximately 550W.
Summarize
The return of the AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 processor heralds a new era in high-end desktop (HEDT) computing. This processor leverages the Zen 4 core architecture, offering up to 64 cores and 128 threads, resulting in formidable multi-core computing performance. It boasts a maximum DDR5 RDIMM memory capacity of 1TB and supports EXPO overclocking memory. With 48 PCIe 5.0 expansion lanes, it caters to the demands of high-end users requiring multi-GPU computing and AI capabilities.
The latest Ryzen Threadripper 7000 processor not only excels in multi-core performance but also stands toe-to-toe with mainstream Ryzen platforms in single-core performance. This ensures that everyday tasks don’t suffer despite the increased core count. While game performance is slightly lower compared to mainstream platforms, the difference remains within reasonable limits.
It’s worth noting that the cost of building a platform around this processor is relatively high. However, for professional users in need of high performance, abundant memory, and extensive I/O expansion offered by the HEDT platform, it’s a worthwhile investment.
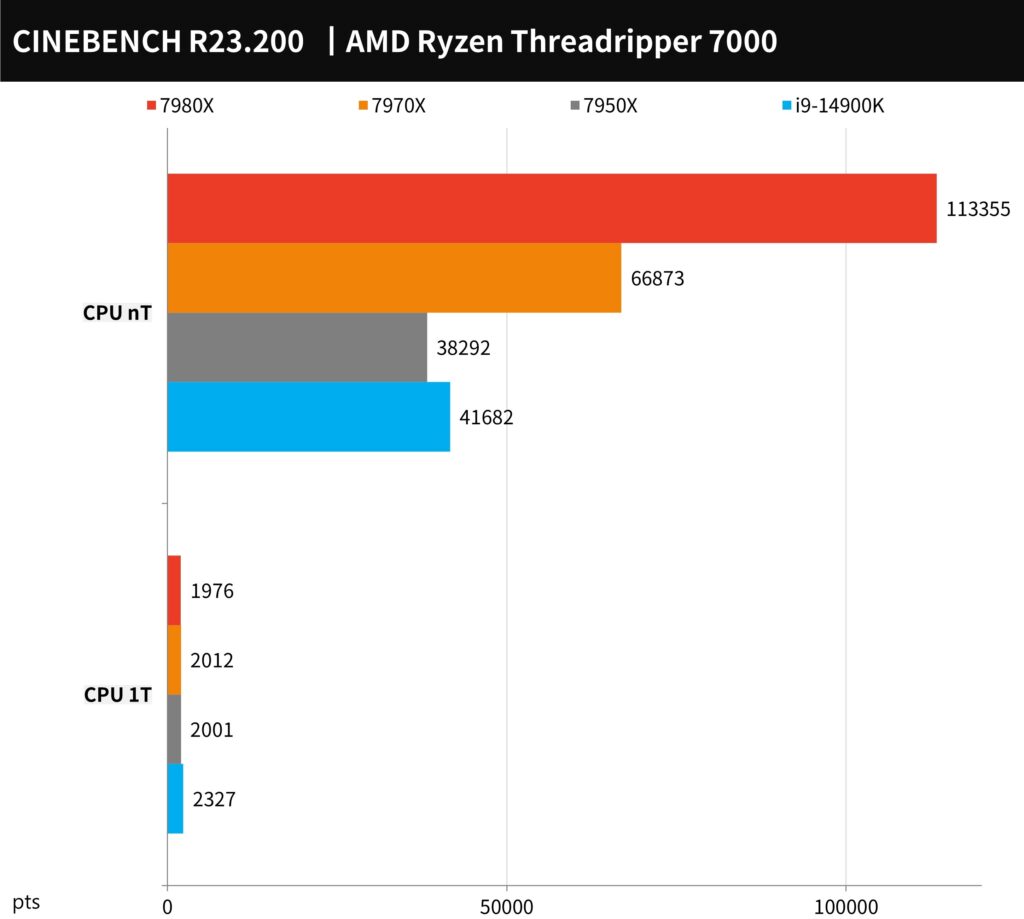
Currently, Intel has not introduced its consumer HEDT platform to the retail market. Previous testing of the Xeon w9-3495X, even when overclocked, achieved a Cinebench R23 score of 83,426 points, which is approximately 36% lower than the multi-core score of 113,355 points achieved by the 7980X, highlighting AMD’s dominance in the consumer HEDT space.
Pricing for the Ryzen Threadripper 7000 series includes the 7980X at $4,999, the 7970X at $2,499, and the 7960X at $1,499. Availability in retail channels will depend on high-end HEDT orders and market demand.
If this article is helpful for you, please share this article with your friends on social media. Thank you!
This article is based on the personality of the reviews. You are responsible for fact-checking if the contents are not facts or accurate.
Title: Revolutionizing High-End Desktops: AMD Ryzen Threadripper 7000 Series Unveiled with 7980X, 7970X, and 7960X Models